All about Viral Fever- Don’t miss out
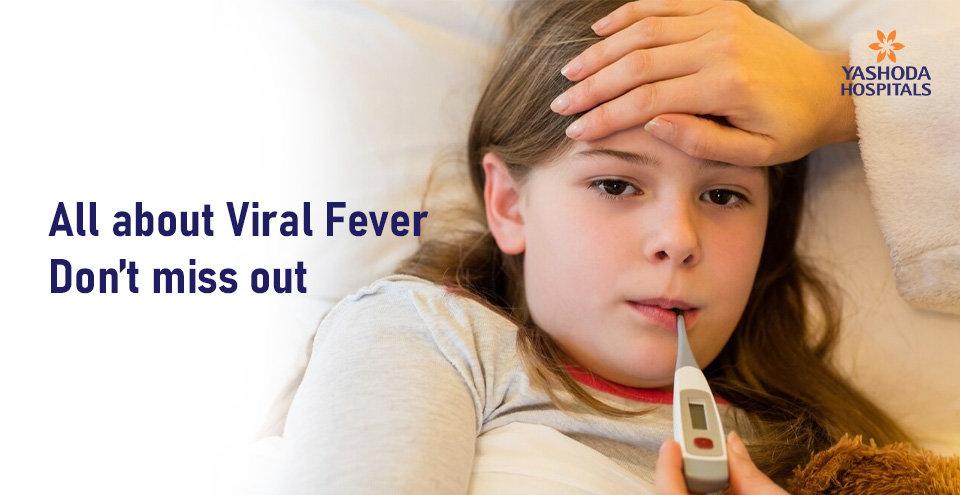
What is viral fever?

Viral fever is a collective term used for fever originating from a variety of viral infections. The average human body temperature is 98.4°F (37.1°C). Any degree of temperature above average is considered a fever. Classified into low-grade (below 100°F) in a few infections, and high-grade (above 100°F) in viral infections such as Dengue, etc.
Viral fever is usually acute, underlying viral infection and more common during season changes, e.g. Monsoon, lasting for 3-5 days of duration; in few severe cases, fever can last up to 14 days. Most common in kids and people with weak immunity, and at times, fever can go undiagnosed, and it could develop into severe complications. It should not be overlooked if you have a fever; you should seek medical care to diagnose and identify the infection. We recommend you consult our team of medical experts if you experience fever.
What are the symptoms of viral fever?

Symptoms associated with a viral fever can vary depending on the type of the viral infection and can also vary from person to person as follows:
- High-grade fever (can go up to 103-104°F)
- Headache (mild to severe)
- Sore throat
- Runny nose or nasal congestion
- Muscle pain (myalgia) and joint pain (arthralgia)- mild to severe
- Dehydration
- Diarrhea or/and abdominal pain
- Nausea / Vomiting
- Fatigue and Dizziness
- Chills
- Redness (Rashes on skin) or burning of eyes
- Facial swelling
- Loss of appetite
Disclaimer: Most of the above symptoms are common in bacterial fevers too.
Viral fever attacks the immune system, and if left untreated, it could lead to secondary or opportunistic infections. Usually, viral fever is self-limiting, and the symptoms tend to subside or resolve on their own as the cycle of the virus nears its end. But, severe symptoms require immediate medical care to prevent any untoward effect on the body functions, one must consult a doctor and seek medical advice. You can consult our medical care experts for further guidance on the symptoms of viral fever and advice to manage them effectively.
Viral Fever vs Bacterial Fever
There are many kinds of viruses that cause different types of fevers, such as influenza or the common cold. It gives you a high temperature and affects your breathing system where these symptoms will disappear within seven days if treated with some rest and drinking water only. On the other side, bacterial fever is caused by bacteria infecting certain parts of the human body resulting in localized pain. Strep throat or urinary tract infections are some examples of diseases that can lead to this fever. Unlike viral fevers, antibiotics should be used when curing it.
Types of viral fever
The classification of the types of viral fever depends on various factors such as mode of transmission, the severity of the disease, the body organ affected, etc. Viral fever-type will also depend on the type of the virus causing the infection. Broadly, viral fever can be classified as:
- Respiratory viral fever: This viral infection is associated with flu-like symptoms such as cough, cold, sore throat, fever, or body aches. Examples include viral fever caused by the common cold, adenovirus, respiratory syncytial virus infection, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) virus, Covid-19 virus and parainfluenza virus infection.
- Gastrointestinal viral fever: This viral infection is associated with gastrointestinal disturbances such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, vomiting, etc. Examples include viral fever caused by rotavirus, norovirus, astrovirus, and a few adenoviruses.
- Exanthematous viral fever: This viral infection is associated with skin rash and skin eruptions. Examples include measles, chickenpox, chikungunya, rubella, smallpox, etc.
- Hemorrhagic viral fever: This viral infection is associated with damage to the circulatory system. Examples include dengue fever, Ebola, Lassa fever, yellow fever, etc.
- Neurologic viral fever: This viral infection is associated with damage to the nervous system. Examples include rabies, polio, viral encephalitis, and viral meningitis.
The majority of these viral fevers resolve are treated symptomatically. You can consult our medical experts on types, symptoms, causes, prevention, and treatment options.
What causes viral fever?
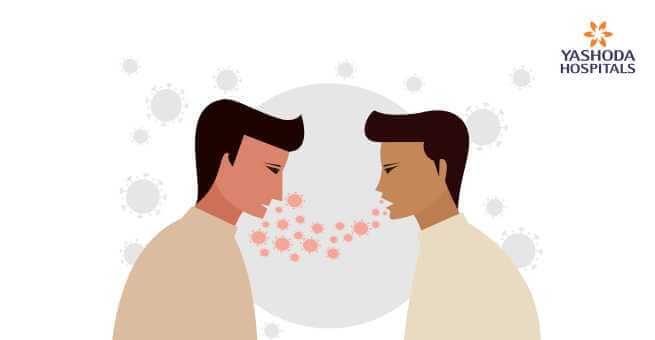
Viral fever is caused by the pyrogens produced in the body when it fights the viral antigens as a defensive mechanism. Causes of viral fever can vary depending upon the type of virus attacking the body.
- Viral fever can be transmitted from one person to another via close contact with the host (the one with active viral infection) or a carrier (the one who might not have the symptoms of the viral fever but is carrying the virus).
- Viral fever can also be transmitted by inhaling the virus-containing droplets from an infected person. Seasonal flu is the most common cause of viral fever.
- Sharing food or drinks with a virally infected person can also transmit viral fever.
- Contaminated water is also a contributory source of viral fever, especially in children.
- Viral fever also spreads by coming in contact with the bodily fluids of an infected person during sexual intercourse.
- Insect (mosquitos and ticks) and rodent (mice) bites can transmit the virus from these animals/insects to humans that cause viral fever. Dengue, yellow fever, Zika, and Chikungunya are viral infections transmitted by animals/insects.
- Exchange of blood with an infected person during drug abuse can also lead to viral fever.
Get the right treatment for viral fever and stay healthy with our specialized care.
How are viral fevers diagnosed/treated?

Identifying a viral fever becomes a complicated task because it shares many common symptoms with bacterial infections. For your doctor to get the right picture through understanding your personal peculiarities, he or she will question your symptoms, the time-frame, and the degree of severity. They might take blood, urine, or swab tests, and evaluate the amounts of white cells. Tests for Dengue, Malaria, Typhoid, or Chikungunya can also be recommended. Lab tests play a crucial role in detecting viral infections.
The treatment received will depend on the virus and the symptoms that one is presenting with. Paracetamol or ibuprofen might be the first to be given to a patient if the case is mild. Acetaminophen may also be given to the patient with a fever who is not a child who has been given paracetamol to decrease fever. Antibiotics may be given either due to primary infections or as a form of preventive treatment. Taking wrong medication is life-threatening, so it is very important to avoid self-medication. The second step is the medical consultation. Get your medical attention soon from a doctor to a proper diagnosis and treatment.

What is the best antibiotic for fever and cold?
Certainly, antibiotics are not best used for colds and fever. The reasons are very simple – the cause for these diseases is caused by a virus hence antibiotic drugs can only work against bacterial infections. When people use antibiotics to treat viral illnesses, they might develop resistance to the drug and may also experience side effects. Penicillin may be prescribed for strep throat while trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole can be used to treat urinary tract infections among others.
Even after multiple counseling sessions, the most frequently asked question is: which antibiotic is best for fever? In view of this, it is highly recommended to take rest, drink plenty of water and use over-the-counter medicines for symptomatic relief like ibuprofen or acetaminophen. If the symptoms persist, become severe or worsen then it is important to see a healthcare provider who will check if there is any bacterial infection present which could need an antibiotic treatment.
Dos & Don’ts during viral fever

Dos
- Take proper rest.
- Drink plenty of liquids to prevent dehydration and maintain electrolyte balance.
- Take your fever or pain-killer medication at prescribed time intervals to avoid pain or discomfort.
- Take your antiviral medicine religiously as prescribed to clear the virus load quickly.
- Eat healthy and light meals that are easy to digest and nutritious.
- Add immunity boosters to your diet such as vitamin C, zinc, honey, etc.
- Maintain personal hygiene and keep your surroundings clean.
- Properly dispose of used tissues that contain your secretions.
Don’ts
- Do not self-medicate without proper medical knowledge of medications and dosages, leading to harmful consequences and worsening the disease.
- Do not take antibiotics unless prescribed by your doctor. Unnecessary use of antibiotics leads to antibiotic resistance, and you might require stronger antibiotics next time you get an infection.
- Do not stay in extremes of temperature such as too cold or too hot because extremes make your body more sensitive and lead to chills or sweats.
- Do not use too many layers of clothes or blankets if you feel chills.
- Do not share your handkerchief, clothes, towels, food, or beverages, as this will inhibit the further spread of the infection to people in contact with you.
How to prevent viral fever?

“Prevention is better than cure,” this is especially true when it comes to viral fevers. It is the viral infections that are at the core of the problem for which prevention is key to avoid the onset of viral fever. Here are some essential tips:
- Maintain Personal Hygiene: Regularly wash and sanitize your hands, avoiding touching your face, change clothes daily, and dispose of used tissues promptly. Refrain from sharing food, drinks, and personal items to minimize viral spread.
- Eat Healthy and Warm Foods: Cold is favorable for virus multiplication, hence, the consumption of warm, high-quality foods reduces the possibility of viral fever. Best food for viral fever is incorporating immune-boosting supplements into your daily diet to improve the rate of protection, and must vaccinate with flu shot which is the most critical step for avoiding flu and virus-induced fever.
- Get Flu Vaccinations: Annual flu shots are wonderful for preventing viral infections that can lead to viral fever.
- Protect Against Mosquitoes: Keep mosquitos away from the infection of the virus by using repellents, mosquito nets and wearing long dresses.
- Seek Timely Medical Care: The importance of the accuracy of diagnosis and the right treatment at the early stage of the disease is the greatest issue in managing viral fever. For the professional services to prevent the diseases, you can contact our expert medical consultants.
When Should I see a doctor?

Most infectious fevers are slight and are healed without severe symptoms or high fever on their own. Yet, consult a doctor if your child’s rectal temperature goes above 100.4F or your own temperature is 103°F or higher. The pediatrician can be consulted if the baby has viral fever for up to two weeks, which may mean that an additional infection has developed.
If you face difficult symptoms the doctor should be approached ten times in case of shortness of breath, chest pain, or extreme headache, and if the symptomology is expressed as nausea or vomiting, diarrhea, rashes that are getting worse, seizures, confusion, neck stiffness, and severe dehydration. The practice of self-medication should be stopped and a doctor should be consulted for accurate diagnosis so that the treatment can be started as soon as possible.
References:
- https://www.cdc.gov/flu/symptoms/flu-vs-covid19.htm
- https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/index.html
- https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/how-can-i-avoid-getting-the-flu?gclid=Cj0KCQjwt-6LBhDlARIsAIPRQcKlph0fPRhkmUU-7f0ndHgB6vCL7dzBy7eNuWGKRuN2xKc2TRe1pJgaAmYBEALw_wcB
- https://www.cdc.gov/flu/index.htm
- https://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0020/153380/flu_case_management.pdf%3Fua%3D1
- https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/question-and-answers-hub/q-a-detail/coronavirus-disease-covid-19-similarities-and-differences-with-influenza
- https://www.dukehealth.org/blog/it-bacterial-infection-or-virus
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4270245/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25962244/














 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More