What are the first signs of pancreatic cancer? How long does a person live with pancreatic cancer?
At a Glance:
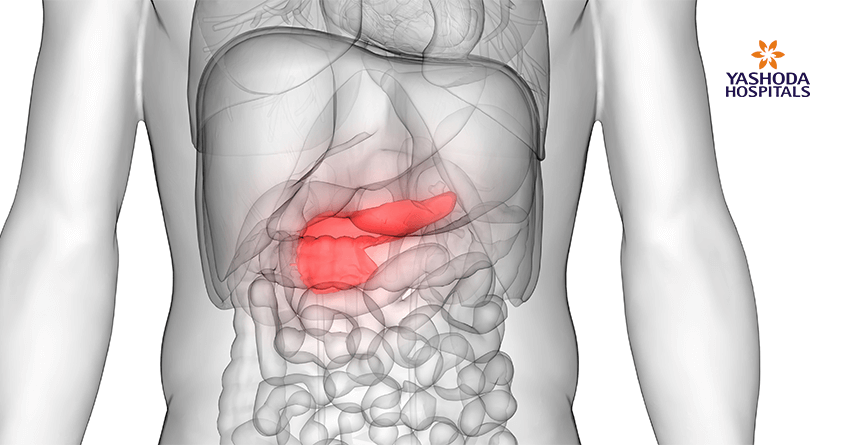
What is pancreatic cancer (PC)?
What are the main causes of pancreatic cancer?
What food causes pancreatic cancer?
What are the signs & symptoms of pancreatic cancer?
What are the risk factors of pancreatic cancer?
What are the stages of pancreatic cancer?
How do doctors diagnose pancreatic cancer?
What are the treatment options of pancreatic cancer? Is pancreatic cancer curable with chemotherapy?
When can surgery in pancreatic cancer not be done?
Is pancreatic cancer always fatal? Why is it fatal?
What are the survival rates of pancreatic cancer?
What is pancreatic cancer (PC)?
Pancreatic cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the tissues of the pancreas. There are two types of pancreatic cancer:
- Adenocarcinoma – This is the most common type of pancreatic cancer, which arises from the exocrine glands i.e in the cells that line the ducts of the pancreas. It is the most aggressive cancer, and difficult to diagnose. By the time the cancer is diagnosed, the disease generally spreads to other organs of the body.
- Pancreatic neuroendocrine carcinoma – This arises in the hormone-producing cells which is the endocrine glands and are less common than adenocarcinoma. It is also known as islet cell tumors or pancreatic endocrine cancer. Pancreas is an important part of the digestive system. It is an organ located behind the stomach and in front of the spine. The pancreas is divided into four anatomical parts; head, extension of the head, body and the tail. It is responsible for carrying out two functions of the digestive system.
- Exocrine functions – The pancreas secretes digestive enzymes that are responsible for the digestion of food.
- Endocrine functions – The pancreas also secrets hormones, such as insulin that is responsible for the control of blood sugar level in the body.
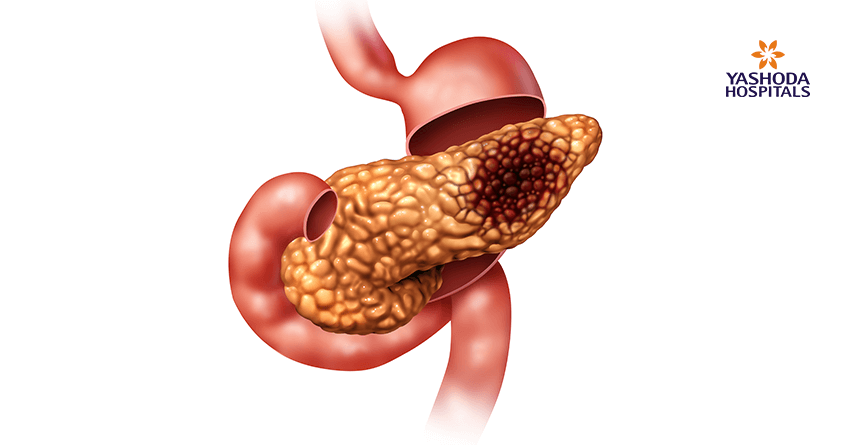
What are the main causes of pancreatic cancer?
While it may not be possible to identify the exact reason for a specific person to develop pancreatic cancer, biological principles of cancer development may help in understanding the underlying reasons. Further, large population-based studies generally help in understanding the role of the various risk factors for pancreatic cancer.
Pancreatic cancer is a disease that is primarily caused due to damage to the DNA i.e deoxyribonucleic acid, the carrier of genetic information. The damage to DNA in scientific terms is often referred to as mutations. Generally these mutations can be inherited by a child from either of the parents or they can be acquired as a person ages. Pancreatic cancer is also considered to be a result of these mutations in the DNA.
What food causes pancreatic cancer?
While there is no certain evidence of any specific food item that may cause pancreatic cancer. Studies have suggested that there may be some link of the disease with diets that may be high in
- Meats
- Cholesterol
- Fried foods
- Nitrosamines etc
On the contrary, diets high in fruits and vegetables may be considered to reduce risk. The vitamin folate may have a protective role to play.
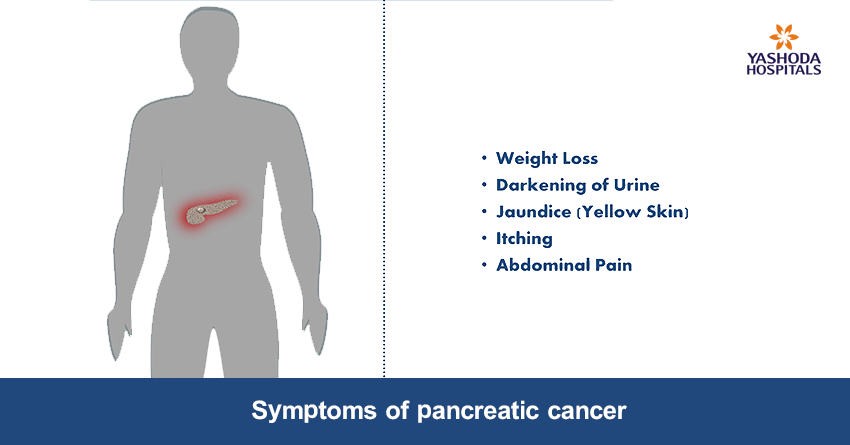
What are the signs & symptoms of pancreatic cancer?
Early signs and symptoms of pancreatic cancer may not be very evident. However, in advanced stages, some of the following signs and symptoms can be present:
- Loss of appetite
- Early clotting of blood
- Depression
- Diarrhea
- New-onset Diabetes
- Gall bladder enlargement
- Feeling of tiredness and weakness
- Persistent upper abdominal pain
- Shortness of breath without much effort
- Yellowish discolouration of skin and eyes (Jaundice)
- Unintended weight loss
Since these signs and symptoms are common in occurrence and may be associated with other medical conditions as well, diagnosis of pancreatic cancer may become difficult.
What are the risk factors of pancreatic cancer?
As stated earlier, there are no specific causes of pancreatic cancer, but some factors that can increase the risk of developing pancreatic cancer include:
- Age – Older age have a higher risk of developing pancreatic cancer
- Obesity i.e. being overweight
- Diabetes
- Family history – Risk increases with presence of disease in the same family
- Pancreatitis – Long term inflammation of the pancreas
- Smoking
What are the stages of pancreatic cancer?
The stage of a pancreatic cancer is determined based on the extent of growth and spread in the body. Stating of the cancer also helps the oncologist to decide the treatment plan.
Staging of pancreatic cancer is done using American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) Tumor, Nodes, metastasized (TNM) system:
- T- stands for “tumor” and determines the tumor growth inside the pancreas or nearby vessels
- N- stands for “nodes” and determines the spread of cancer to nearby lymph nodes
- M- stands for “metastasis” and determines the spread of cancer to distant lymph nodes or distant organs of the body such as liver, abdominal cavity, lungs and bones.
Based on the growth and spread of the tumor in the body, staging is also done in 4 stages, Stage I up to Stage IV, ranging from localization of the cancer only till the pancreas to higher number showing spread of cancer to the lymph nodes or other organs of the body.
- Stage 0. Known as cancer in situ, i.e “in place”, it means that the cancer is localized in the place of initiation and no spread to nearby tissues. Cancer in this stage is mostly curable.
- Stage I. Indicates a small cancer or early stage cancer which has not grown much in the adjacent tissues or has not spread to the lymph nodes or other parts of the body.
- Stage II and Stage III. Indicate larger cancers or tumors that may have grown deeper into adjacent tissues. They may have also spread to lymph nodes but not to distant parts of the body.
- Stage IV. Indicates the spread of the cancer to distant organs or parts of the body. It is usually known as advanced or metastatic cancer.
How do doctors diagnose pancreatic cancer?
Diagnosis of pancreatic cancer is not easy as physical signs and symptoms may not be evident in the early stages and when present, they are very obscure. Thus, awareness on the patient’s part is very important. Thus, if you have a family history of pancreatic cancer or have suspected signs and symptoms visit a doctor and voice your concerns. If the doctor suspects the occurrence of pancreatic cancer, you may be referred to an oncologist for further evaluation. Diagnosis can be made by:
- Medical History: Referring if any of the symptoms the patient had suffered in the past related to the signs and symptoms of pancreatic cancer.
- Family History: In case there is anyone in the family such as parents or grandparents who had been suffering from pancreatic cancer or any other cancers
- Tests as may be required:
- Biopsy: a small sample of the tissue is removed from the pancreas and observed under a microscope
- Blood test: sample of the blood is tested for specific protein which is a tumor marker.
- Computerised tomography (CT) scan
- Magnetic Resonance tomography (MRT) scan
- Positron Emission tomography (PET) scan
- Ultrasound
- Endoscopic ultrasound
What are the treatment options of pancreatic cancer? Is pancreatic cancer curable with chemotherapy?
The treatment options for pancreatic cancer are based on the type and stage of pancreatic cancer and other factors like overall health, age, and sensitivity to certain medications. Some of these options that may be used in combination include:
Surgery Depending on the extent of spread, surgery for pancreatic cancer may include the following:
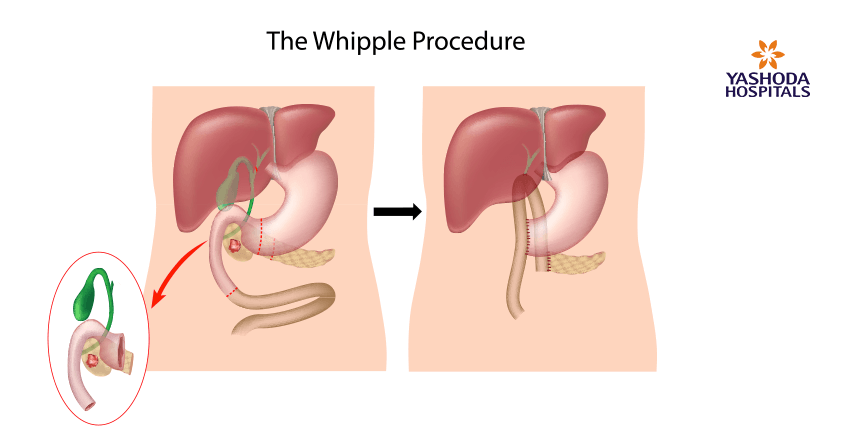
- Pancreaticoduodenectomy: Removal of the head of the pancreas, a part of the small intestine, the gallbladder and a part of the bile duct. This procedure is also called the Whipple procedure.
- Distal pancreatectomy: Removal of the body and the tail of the pancreas
- Pancreatectomy: Removal of the entire pancreas
Radiation therapy: Use of high-powered energy beams to destroy cancer cells.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy (chemo) is a conservative therapy often used for the treatment of certain cancers. It makes use of anti-cancer drugs that are either injected into a vein or administered by mouth. The chemo drug reaches all areas of the body through the bloodstream. This treatment option is thus potentially useful for cancers that have spread to the other parts of the body from the origin.
Chemotherapy is used in some of the following circumstances of pancreatic cancer:
- Chemo is often administered as a part of the treatment for one of the most common pancreatic cancer i.e exocrine pancreatic cancer. However, in case of other forms of pancreatic cancer like the neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), other types of medicines may be used more often.
- Chemo may be indicated at any stage of pancreatic cancer.
- Neoadjuvant treatment: Chemo can be given before pancreatic cancer surgery with or without radiation in order to shrink the tumor.
- Adjuvant treatment: Chemo can be given after pancreatic cancer surgery with or without radiation to kill any cancer cells that may have been suspected to be left behind after the surgery. With this type of treatment, the chances of recurrence of the tumor are reduced.
- Chemo is also often advised in case of an advanced pancreatic cancer that can’t be removed completely with surgery. It may also be indicated in cases where surgery is not feasible for some reason like the poor medical condition of the patient.
Chemoradiation or chemoradiotherapy: When chemo is administered along with radiation, it accentuates the effect of radiation. However, sometimes, there can also be more severe side effects.
Palliative care– Intended to improve the quality of life of cancer patients who may not be amenable to treatment.
When can surgery in pancreatic cancer not be done?
Based on the stage the tumor doctors generally decide if tumor can be removed or not. While surgery may not be feasible in cases where the patient’s medical condition doesn’t warrant it, there are three possible options depending on the stage of the pancreatic cancer:
- Resectable: The option when the cancer can be removed in case the disease has not spread to nearby blood vessels, lymph nodes or organs, which is usually at the early stage of cancer.
- Borderline resectable: In this case the tumor might have just spread to nearby blood vessels. The doctors can analyze the cancer and decide if surgery can be done or not.
- Unresectable: This is the advanced stage of diagnosis wherein surgery cannot be taken place as the cancer has spread to distant or nearby blood vessels or other organs of the body.
Is pancreatic cancer always fatal? Why is it fatal?
Pancreatic cancer is often fatal and it is ranked as fourth deadliest cancer in both men and women. Pancreatic cancer is treatable when diagnosed early and fatality rates are minimal. However, a vast majority of cases are diagnosed in later stages. pancreatic cancer is difficult to diagnose because of lack of reliable screening test and vague symptoms that are easily confused with other diseases making the diagnosis difficult and delayed.
What are the survival rates of pancreatic cancer?
The treatment of pancreatic cancer becomes difficult in advanced stages. Most of the cases are detected after the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. Therefore, the chances of survival are very less. As per the national cancer database, 12.6 months is the overall median survival for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Based on the current treatment modalities, only 5 in 100 pancreatic patients survive for five years after diagnosis.
Knowledge of suffering from cancer can be distressing, frustrating and depressing. Therefore, few measure should be taken to improve the quality of life, such as:
- Connecting with other cancer-survivors
- Discussing the distress with a doctor
- Being more aware on pancreatic cancer and care that can be taken
- Getting involved in social groups
- Meeting friends and family
- Often talking with someone
- Supportive therapies can also cope with relieving distress
- Being spiritually active
- Daily exercise
- Music therapy
- Yoga and meditation
How can pancreatic cancer be prevented?
While there are no known preventive measures for pancreatic cancer, individuals who have a known family history of the disease, can work on leading a healthy lifestyle to reduce the risk. Some of these measures include:
- Regular screening
- A healthy diet- comprising of fresh vegetables, fruits and whole grains
- Avoid smoking
- Regular exercise
Conclusion:
Pancreatic cancer is one of the deadly cancers, we still believe that there is always hope. Patients with pancreatic cancer can hope for a good quality of life with love and care from family and friends and quality treatment for good clinical response. Increasing evidence is suggestive of the fact that the most effective care for patients with pancreatic cancer can be provided with a multi-disciplinary team approach. Coordinated care from doctors of different specialties including general physician, oncologist, radiation oncologists, oncosurgeons, dieticians, gastroenterologists and pathologists can result in better outcomes for complex cancer treatment.
Were we able to address your queries about Pancreatic cancer?
For more information please request a callback and our health experts will get in touch with you.
References:
- Mayo Clinic. Pancreatic Cancer. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pancreatic-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20355421. Accessed on 05 October, 2018
- American Cancer Society. Signs and Symptoms of Pancreatic Cancer. Available at: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/pancreatic-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/signs-and-symptoms.html. Accessed on 05 October, 2018
- Medline Plus. Pancreatic cancer. Available at: https://medlineplus.gov/pancreaticcancer.html. Accessed on 05 October, 2018
- John Hopkins Medicine. Pancreatic cancer. Available at: http://pathology.jhu.edu/pancreatic cancer/MDC/index.php. Accessed on 05 October, 2018










 Appointment
Appointment Second Opinion
Second Opinion WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More





