All You Need To Know About Pacemaker Surgery
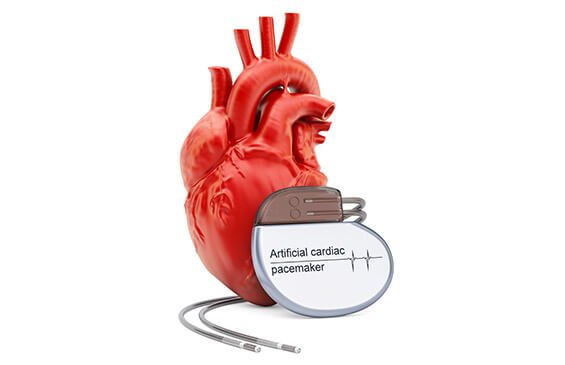
A pacemaker is a small implantable medical device that helps regulate the heart rhythm. It helps in managing conditions associated with the electrical system of the heart, when any part of the conduction system of the organ fails. Its major function is to ensure that the heart does not beat too fast or too slow, and beats at the right rhythm to avoid arrhythmias.
It is placed under the skin below the collar bone and connected to the heart chambers by lead wires running through a blood vessel. This surgery usually takes 1 to 2 hours.
How much does a Pacemaker Surgery cost in India?
The average cost of pacemaker surgery in India is usually between Rs. 2,75,000 to Rs. 3,00,000. The device costs anything between Rs.45,000 to Rs.1,50,000. However, the prices may vary depending upon the hospitals in different cities.
What is the average cost of Pacemaker Surgery in Hyderabad?
The cost of pacemaker surgery in Hyderabad starts from Rs.52,200. Yet, it depends upon multiple factors.









 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More

