Facts about iMRI aided surgeries for brain tumour and diseases
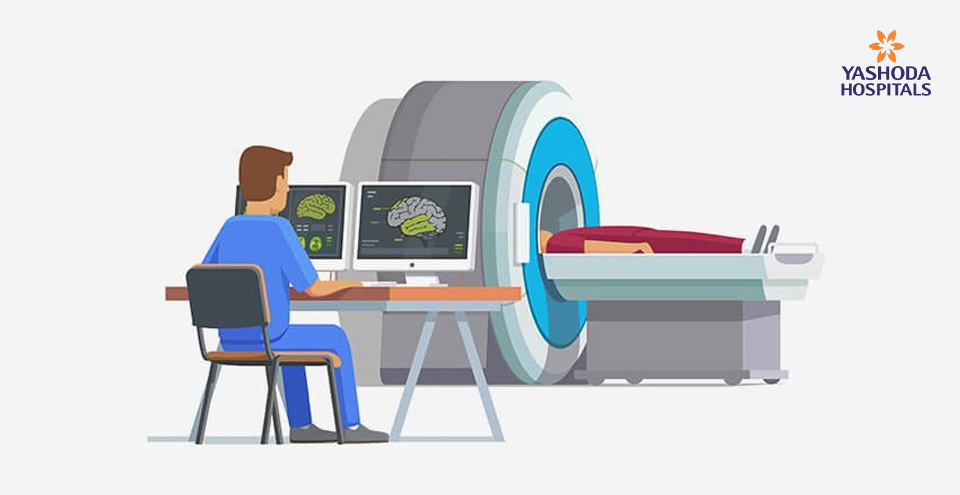

Neurological diseases affect a person’s ability to do deal with school, work and personal tasks independently. Immediate rectification of anomalies in brain such as tumors, clots, embolism is possible with brain surgery. However, brain anomalies located in deep and hard-to-reach regions are precisely corrected using image guided surgeries. The image guidance help the neurosurgeons with magnified image and minute detailing so the healthy tissues are unharmed in the process.
What are different types of brain diseases?
Common diseases of the brain may be of the following types:
Infections of the brain like:
- Abscess of brain: Formation of pus within the brain due to some bacteria
- Encephalitis and meningoencephalitis: Viral induced inflammation of the brain tissues
- Meningitis: Inflammation of the lining of the brain or spinal cord attributed to infection
Seizures:
Epilepsy is the most common cause of seizures. Stroke, infections and head injuries may also lead to seizures.
Trauma:
Injuries of the skull due to accidents, falls etc may have an impact on the brain. Some of these conditions include:
- Concussion: A compression of the brain without any structural damage may lead to only temporary problems like memory loss, temporary paralysis etc.
- Traumatic brain injury may sometimes cause permanent brain damage leading to conditions like paralysis, personality changes etc.
- Intracerebral haemorrhage: High blood pressure, rupture of blood vessels due to deformity or trauma etc

Tumours, masses, and conditions due to increased pressure:
- Tumours:Any abnormal growth of the tissue within the brain is called a tumour. Tumours can be malignant tumours or benign tumours. Sometimes the brain tumour symptoms appear due to pressure of the tumour growth on the neighbouring structures. Common types of brain tumours are glioblastoma, meningioma, acoustic neuroma, glioma, carcinoid tumour, neuroendocrine tumour, medulloblastoma, etc.
- Hydrocephalus:Sometimes, due to an abnormal circulation, the fluid inside the skull may increase abnormally, thus creating a pressure.
Brain diseases connected with blood vessel conditions include:
- Brain aneurysm
- Cerebral oedema
- Cerebrovascular accident (CVA)
- Epidural haematoma
- Intracerebral haemorrhage (bleeding inside the brain)
- Stroke: may be ischemic or haemorrhagic
- Subdural haematoma
- Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
Brain diseases due to autoimmune conditions include:
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
- Vasculitis
Brain diseases due neurogenerative conditions include:
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Dementia
- Huntington’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease
- Pick’s disease (frontotemporal dementia)
What conditions require brain surgeries?
The brain is the centre of body’s control and coordination in both conscious and unconscious states. However, it is an extremely delicate organ, and prone to long lasting effects from bleeding, infection, trauma and structural damage. As a result, some conditions may require brain surgery i.e neurosurgery, performed by neurosurgeons to diagnose or treat such problems.
Some of the common symptoms of conditions that may need brain surgery include:
- Headache
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Drowsiness
- Seizures
Some of the common indications for brain surgery are alterations in:
- Structure of brain tissue due to brain cancers, infections and oedema
- Blood flow to the brain due to subdural haematoma, subarachnoid haemorrhage and intraventricular bleed etc.
- Compositions or amount of cerebrospinal fluid from infection or hydrocephalus
- Brain cancer like gliomas, pituitary tumour, acoustic neuroma or schwannoma, medulloblastoma, lymphomas, chordomas, metastases or secondary tumours etc.
How are conditions requiring brain surgery diagnosed?
A condition that needs brain surgery should not be delayed as it can cause further, sometimes permanent damage to the brain, even death, if untreated. Surgeries like tumour removal from brain is a high precision brain surgery. Hence it is necessary that a hospital offering such services should have neurosurgeons with hands-on-experience for accurate removal of tumour and correction of brain deformities, a team of expert anaesthetists, neurologists and support staff along with advanced technology and infrastructure support.
Diagnosis of conditions requiring brain surgery can be made by:
- Medical history
- Physical examination
- Tests:
- CT scan
- MRI scan etc
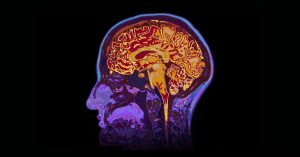
What is iMRI brain surgery? How is it different than traditional brain surgeries?
Intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging (iMRI) is one of the latest and cutting edge technology in neurosurgery. In this procedure, images of the brain are created during the surgery. Accurate pictures of the brain help the neurosurgeon in easy visualization during operations.
In comparison to traditional brain surgeries, iMRI has the following advantages:
- Real-time images created with iMRI are vital, as they help in accurately identifying the location of the brain abnormalities. During surgery, the brain may shift in position, thus the location of the defect may also change. Pre-treatment images in such cases become useless.
- The edges of a brain tumour may not be very clearly differentiated in the traditional surgery. However, with iMRI, it is possible to clearly separate normal tissue from abnormal tissue. A successful removal of the entire brain tumour can be confirmed from the images.
- Compared to traditional surgery, iMRI brain surgeries have shown improved outcomes and reduced cost burden.
- Since it enables real time correction of the nerve defects, nerve function can be evaluated during the operation. Thus, patients can now undergo complete treatment in one single operation.
Uses for iMRI
iMRI is being used for many surgeries like:
- Brain tumours
- Dystonia
- Epilepsy
- Essential tremor
- Glioma
- Neuropsychiatric disorders
- Parkinson’s disease
- Paediatric brain tumours
- Pituitary tumours
To know more about brain surgeries, you can request for a call back and our experts will call you and answer all your queries.
References:
- Mayo Clinic. Intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging (iMRI). Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/intraoperative-magnetic-resonance-imaging/about/pac-20394451 Accessed on March 18, 2018
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. Neurology and Neurosurgery. Available at:https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/neurology_neurosurgery/centers_clinics/ionm/types/intraoperative-mri.html Accessed on March 18, 2018
- UCLA Health. MRI Suite (Intraopperative). Available at: http://neurosurgery.ucla.edu/mri-suite-intraopperativeAccessed on March 18, 2018















 Appointment
Appointment Second Opinion
Second Opinion WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More





