Hydrocephalus, a most common reason for brain surgery in kids
At a Glance:
2. What are the signs and symptoms of hydrocephalus?
3. What are the types of hydrocephalus?
4. What are the causes of hydrocephalus?
5. What are the risk factors of hydrocephalus?
6. How is hydrocephalus diagnosed by doctors?
7. What are the treatment options for hydrocephalus?
8. What are the complications of hydrocephalus?
9. Is it possible to prevent hydrocephalus?
10. How should one choose a hospital for hydrocephalus?
11. What is the outcome or prognosis of hydrocephalus treatment?
What is hydrocephalus?
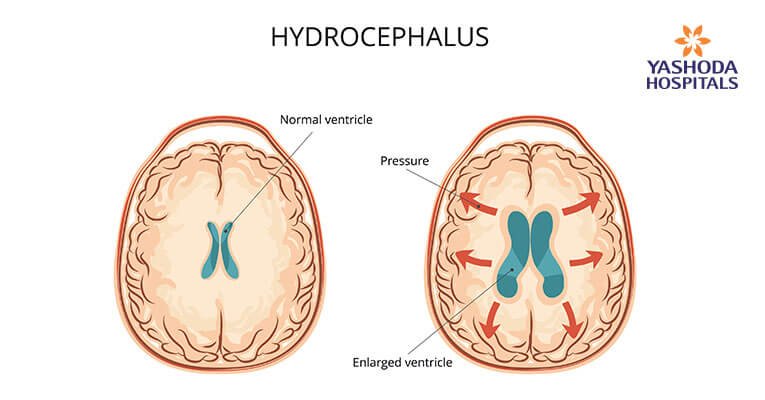
Hydrocephalus is a medical condition which occurs when the amount of cerebrospinal fluid starts increasing, causing an increase in the pressure in the brain. The excess fluid also increases the size of the ventricles. Increase in pressure damages the brain tissue and results in the abnormal functioning of the brain.
Cerebrospinal fluid is secreted in the brain by tissues lining the ventricles. It performs various functions such as keeping the brain buoyant, preventing brain injury by acting as a cushion, keeping the brain and tissues clear of waste products and helping to maintain a constant pressure within different parts of the brain. In a normal person, the pressure created due to cerebrospinal fluid is constant. This is because the amount of fluid secreted is in balance with the amount of fluid removed by absorption through blood vessels. The fluid easily moves from one ventricle to another with the help of channels.
What are the signs and symptoms of hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus can occur at any age, and it manifests differently at different ages. The signs and symptoms of this condition depend upon the age, and the ability of the person to accommodate increased pressure.
Signs and Symptoms in Infants: As the sutures (joints within the bones of the skull) of infants are not closed, increased pressure is accommodated by expanding the circumference of the skull. The most common sign/symptom of hydrocephalus in infants is large head size. Other signs and symptoms of hydrocephalus in infants include:
- seizures
- poor appetite
- drowsiness
- irritability
- vomiting
- thin scalp.
Signs and Symptoms in Children: The signs and symptoms for children are almost similar to those in infants. Symptoms of hydrocephalus in children include sleepiness, blurred or double vision, sleepiness, delayed developmental milestones, poor learning at school, seizures, abnormal sensory-motor functions, and ‘setting sun’ eyes. There might be a change in personality, and the child may have a problem in previously acquired activities such as talking.
Signs and Symptoms in Adults: Two types of hydrocephalus: congenital hydrocephalus and normal pressure hydrocephalus are found in adults. The common signs and symptoms include:
- nausea
- vomiting
- drowsiness
- headache.
- The person may also have memory loss, cognitive dysfunction, poor balance, and loss of bladder control.
What are the types of hydrocephalus?
There are various ways to classify hydrocephalus. On the basis of the underlying cause, hydrocephalus is classified as follows:
Obstructive hydrocephalus: In this type of hydrocephalus, cerebrospinal fluid does not flow freely between the ventricles due to malformation or narrowing of the channels.
Non-obstructive hydrocephalus: This type of hydrocephalus is caused when the cerebrospinal fluid is not sufficiently absorbed by the tissues, leading to an increased level of the fluid.
Ex-vacuo hydrocephalus: This is caused due to injury or a stroke. In most of the cases, treatment is not required in Ex-vacuo hydrocephalus.
Hydrocephalus may also be classified as follows:
Depending on the timing of its occurrence, hydrocephalus is classified as:
Congenital hydrocephalus: This condition is present at birth. The condition may be caused due to infection or effect of teratogens. It also found concomitantly with other disorders such as neural tube defects.
Acquired hydrocephalus: This form of hydrocephalus is acquired after birth. This may be caused due to infection, injury, or tumour.
Normal Pressure hydrocephalus: This form of hydrocephalus is commonly found in persons of age 55 years and older. The condition results in a decline in memory and cognitive dysfunction. Causes include infection, injury, and bleeding within the brain.
Hydrocephalus in adults: Normal pressure hydrocephalus and ex-vacuo hydrocephalus are found in adults. It has been estimated that almost 5-6% of dementia cases are due to normal pressure hydrocephalus.
Hydrocephalus in babies: Hydrocephalus in babies is characterized by increased head circumference to accommodate for increased pressure. Other symptoms include swelling veins, split sutures, and downward setting of eyes.
What are the causes of hydrocephalus?
Cerebrospinal fluid normally flows within the ventricles and channels before finally being absorbed in the bloodstream. Any problem in either flowing through ventricles or absorption in the bloodstream results in increased pressure inside the skull. This causes damage to brain tissues. Hydrocephalus is caused due to:
Obstruction: This is the most common cause of hydrocephalus. When there is any obstruction, either due to malformation or narrowing of channels, the fluid flow stops and is accumulated in the ventricles. This results in increased pressure and causes the symptoms.
Poor absorption: For maintaining normal fluid pressure inside the brain or skull, the process of secretion and absorption are synchronised. However, due to conditions like inflammation of the tissues, cerebrospinal fluid is poorly absorbed in blood vessels, leading to increased volume.
Overproduction: Overproduction is rarely the cause of hydrocephalus. Hydrocephalus may also be caused when the tissues lining the ventricles produce an increased quantity of fluid.
What are the risk factors of hydrocephalus?
A person may suffer from hydrocephalus due to various reasons, but some factors increase the risk of hydrocephalus. Several risk factors are:
Brain Injury: Hydrocephalus is a serious complication of brain injury. It results in an increased mortality rate if the condition is not diagnosed early and treated effectively.
Bleeding in the brain: Bleeding in the brain leads to the formation of a blood clot. This blood clot may block the passage of cerebrospinal fluid and lead to obstructive hydrocephalus.
Infections: Brain has membranes called meninges. In meningitis, these membranes get swollen. Meningitis results in the scarring of meninges. The risk of hydrocephalus increases because of this scarring.
Brain Tumour: Tumours of the brain may cause an obstruction in the flow of cerebrospinal fluid and lead to hydrocephalus. The risk is further increased if the metastases of tumour occur in periventricular brain tissue.
Inappropriate fetal development: Improper development of the central nervous system, including the brain, may result in the obstruction of the flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
Premature delivery: Babies with premature delivery are at high risk of ventricular bleeding that may further cause hydrocephalus.
Pregnancy complications: Pregnancy complications include infection of the uterus, which may result in swelling and inflammation of fetal neural tissues.
How is hydrocephalus diagnosed by doctors?
Hydrocephalus is diagnosed after taking a medical history. This is followed by a physical and neurological examination and imaging tests.
Physical Examination: The doctor will ask various questions regarding the signs and symptoms, medical history, head injury, etc. In the case of infants, the condition is clearer due to large head circumference. The head of the infant expands to normalize the pressure within the brain.
Neurological evaluation: Hydrocephalus causes various abnormalities in the brain because of the damage to brain tissues. The doctor performs various tests to evaluate the severity of the neurological condition:
- Muscle activity test
- Sense organ tests
- Movement tests
These are conducted to evaluate neurological health.
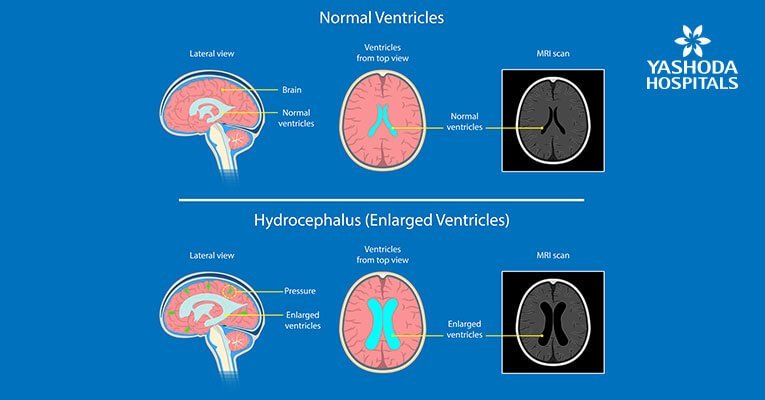
Imaging techniques: Brain imaging tests are performed to identify the cause of hydrocephalus. Further, the imaging tests of a person will show the ventricle being enlarged due to excess cerebrospinal fluid.
Imaging techniques used in the diagnosis of hydrocephalus are:
- Ultrasound
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Computerized Tomography
What are the treatment options for hydrocephalus?
There is no medical therapy to treat hydrocephalus. The only effective treatments are surgical. Depending upon the needs of the person, hydrocephalus can be treated in a variety of ways. Following are some of the surgical options available for treating hydrocephalus:
Direct Treatment: Direct treatment for hydrocephalus includes removing the obstruction that limits the flow of cerebrospinal fluid through the ventricles. This may include reducing the inflammation of the tissues and removing the tumor surgically.
Indirect Treatment: This involves the insertion of a shunt through surgery. The shunt will help in draining the excess cerebrospinal fluid from the brain to other parts of the body, such as the abdominal region. This will help in normalizing the pressure within the brain. The fluid will flow at a predetermined rate and direction. In some cases, both direct and indirect methods are implemented.
Endoscopic third ventriculostomy: Through this surgery, a tube with a camera is inserted into the brain, and the surgeon creates a new way (bypasses the blockage) for the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
What are the complications of hydrocephalus?
Untreated hydrocephalus leads to neurological complications. In many cases, the treatment may not reverse the already damaged tissues and its manifestations, but it may still help in preventing further damage. Doctor’s consultation is immediately required if the person experiences any symptoms related to hydrocephalus. This will help to reduce the damage. The complications of hydrocephalus are:
- Delayed developmental milestones
- Cognitive dysfunction
- Poor coordination and balance
- Vision changes such as double vision
- Seizures
- Lack of focus and concentration
- Dementia
- Speech problems
- Physical and developmental disability
- Death
Is it possible to prevent hydrocephalus?
Although complete prevention of hydrocephalus is not possible, various measures can be taken to reduce the risk of developing hydrocephalus:
Vaccination: Infection is one of the primary reasons for hydrocephalus. Prevention of infection can be done through vaccination. Meningitis vaccine reduces the risk of hydrocephalus by protecting against meningitis. Further, a healthy diet and food that enhances immunity may also be helpful in keeping the infections at bay.
Safety: Prevention of head injuries significantly reduces the occurrence of hydrocephalus. Always wear a seat belt while driving a car and helmets while driving two-wheelers. Safety measures should also be followed while playing games, where chances of injury are high—especially in contact sports. The elderly are at high risk of injury due to falling. Proper care should be taken to prevent injuries to the elderly such as handrails on the staircases or not leaving the bathroom floor wet.
How should one choose a hospital for hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus is a serious neurological disorder, and because of the inherited complexity in hydrocephalus, the treatment and diagnosis should only be done at a highly specialized and state-of-the-art medical facility. It should be equipped with comprehensive patient management and diagnostic facilities. The neurosurgeons of the medical centre should be highly skilled and experienced in performing hydrocephalus surgery, preferably through minimally invasive techniques. Insertion of a ventricular shunt or endoscopic third ventriculostomy should be conducted by using the modern surgical system.
Yashoda Institute of Neuroscience is a pioneer in the field of neurosurgery. The institute is equipped with scientifically advanced diagnostic techniques and surgical equipment complemented with a skilled and experienced multidisciplinary team of neurosurgeons, neurologists, physicians, and paramedical staff.
What is the outcome or prognosis of hydrocephalus treatment?
Prognosis of hydrocephalus treatment depends upon the age of the person, type of treatment performed, and the stage at which the diagnosis was done and the treatment initiated. In some persons, dementia improves after shunting while some patients are not able to recover with the same technique. Prognosis also depends upon the cause of hydrocephalus. It has also been noted that the success rate of treatment is high when the cause of hydrocephalus is known as compared to the condition when the cause remains unknown. Diagnosis at an early stage and initiation of appropriate treatment significantly increases the chances of complete recovery. Untreated and progressive hydrocephalus may result in death.
Read more about Hydrocephalus symptoms, causes and treatment
If you find any of the above mentioned of Hydrocephalus then
Book an Appointment with the best neurologist in hyderabad
References:
- Mayo clinic. Hydrocephalus. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hydrocephalus/symptoms-causes/syc-20373604. Accessed on 5th June 2019
- American Association of Neurological Surgeons. Hydrocephalus. Available at: https://www.aans.org/Patients/Neurosurgical-Conditions-and-Treatments/Hydrocephalus. Accessed on 5th June 2019
- Hydrocephalus Association. Hydrocephalus. Available at: https://www.hydroassoc.org/hydrocephalus/. Accessed on 5th June 2019
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Hydrocephalus fact sheet. Available at: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Hydrocephalus-Fact-Sheet. Accessed on 5th June 2019
- The Nemours Foundation. Hydrocephalus. Available at: https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/hydrocephalus.html. Accessed on 5th June 2019
















 Appointment
Appointment Second Opinion
Second Opinion WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More





