Yashoda Hospitals > Diseases & Treatments > Orthopaedics > Spondyloarthritis – Ankylosing Spondylitis
Spondyloarthritis – Ankylosing Spondylitis
Types, causes, symptoms, complications, diagnosis and treatment
What is Spondyloarthritis? What are the types of Spondyloarthritis?
Spondyloarthritis, also known as spondylitis or spondyloarthropathy, is a group of closely related rheumatic diseases that primarily affect joints and enthesis (ligaments and tendons). It is characterized by inflammatory back pain as well as pain and inflammation of the neck, intestine, pelvis, eyes and large joints in the body.
Spondyloarthritis is an umbrella term which is largely associated with the spine, however, it also includes problems related to inflammation of other areas in the body. The most common conditions of spondyloarthritis are:
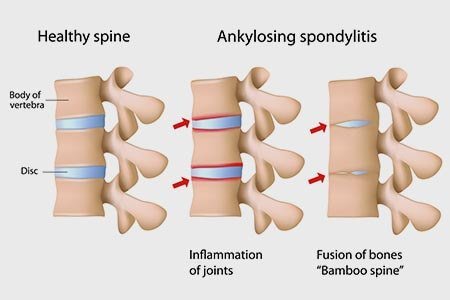
- Ankylosing spondylitis is the inflammation and ankylosis (new bone formation) of the spine resulting in inflammatory back pain.
- Reactive arthritis is the inflammation of joints, skin, eyes, bladder, genitals and mucous membrane that follows after an infection in the intestine or urinary tract. Usually, the symptoms are not permanent and they subside in 3 to 12 months. In some cases, patients may develop chronic arthritis.
- Psoriatic arthritis is the inflammation and ankylosis of spondylitis in the spine and small joints in hands and feet with skin-related symptoms of psoriasis.
- Enteropathic arthritis is characterized by the spine and joint symptoms along with inflammation of the intestine which is associated with inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Juvenile spondyloarthritis: Children with spondyloarthritis (identified with prominent enthesitis) have more peripheral involvement especially in the lower extremity.
- Undifferentiated spondyloarthritis: Spondyloarthritis that does not fit into any of the above types are categorized here.
According to the newer SpA classification system, spondyloarthritis is classified into:
- Axial spondyloarthritis (AxSpA): It is a broad category that includes people with or without characteristic inflammatory changes of the sacroiliac joints (joints linking the lowest part of the spine to the pelvis) in X-ray.
- – Radiologic AxSpA: Spondylitis wherein the sacroiliac changes are prominent on X-ray. Almost all cases of ankylosing spondylitis belong in this category.
- – Non-radiologic AxSpA: Spondylitis without characteristic sacroiliac changes on X-ray.
- Peripheral spondyloarthritis (pSpA): This term covers inflammation in joints and/or tendons outside the spine or sacroiliac joints, such as joints in the hands, wrists, elbows, shoulders, knees, ankles, and feet.






 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More