Robot-Assisted Gynecological Surgeries
Robot-assisted hysterectomy, its benefits, risks, success rates and costs
What are different robot-assisted gynaecologic surgeries such as hysterectomy? When are they recommended?
For years, open surgery, which uses large incision for accessing uterus and surrounding anatomy, has been the standard approach to gynecologic surgeries.
Open surgery is an invasive procedure associated with significant pain, trauma, a long recovery process and damage to surrounding organs and nerves.
With the advent of new technologies, lesser invasive options like laparoscopy are now available. However, with monitors that have a two-dimensional (2D) vision, laparoscopic procedures have disadvantages like lesser in-depth perception, camera instability, limited range of motion. Thus, laparoscopy has its own challenges for delicate and complex surgeries like hysterectomies (removal of the uterus) or endometriosis.
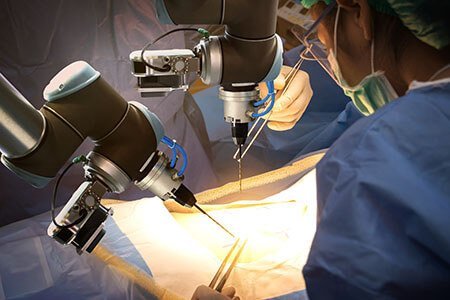
For delicate surgical procedures, the robot-assisted surgery is considered to be the most effective treatment option available today. By making few tiny 1-2 cm incisions, the surgeon operates with greater precision and control. Since the risk associated with large incision is greatly reduced, there is a greater likelihood of a fast recovery and excellent clinical outcomes. Robotic surgery can be performed for various gynecological conditions like:
- Hysterectomy (benign or cancerous) i.e. removal of the uterus
- Myomectomy: for the removal of fibroids from the uterus
- Sacrocolpopexy: surgical correction of vaginal vault prolapses
- Surgery for gynecological cancer
- Oophorectomy and ovarian cystectomy: removal of ovary an ovarian cyst
- Resection of endometriosis
- Lymphadenectomy
- Other surgeries: cervical cerclage, vesicovaginal repair, rectovaginopexy and Burch colposuspension
The robotic surgical system comprises of three components:
- A surgeon’s console
- A patient-side cart with four robotic arms
- A high-definition, magnified (12X), and a 3D vision system
The movements of the surgeon’s hand are mimicked by the instruments attached to the robotic arms, which are smaller in size, and more flexible than the human hand.




 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More