The respiratory system includes organs such as the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea and the lungs. These organs together help in the breathing cycle. Infection caused in these organs is termed as respiratory tract infection (RTI). Depending on the area affected, RTI can be classified into upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) and lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI).
Upper respiratory tract infection– This affects the nose, sinus and throat. Most common upper respiratory tract infections include:
- Common cold
- Sinusitis
- Tonsillitis
Lower respiratory tract infection– This affects the bronchi and lungs. The most common ones are:
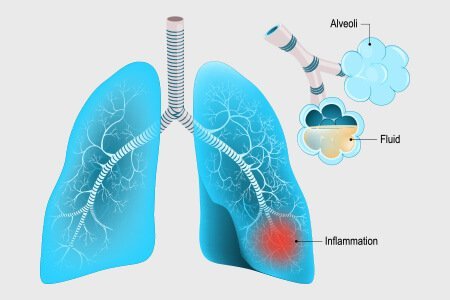
- Pneumonia: It is very common in children/babies and it is further classified into;
- Community-acquired pneumonia: Acquired outside of the hospital or healthcare facilities
- Hospital-acquired pneumonia/ Healthcare-acquired pneumonia: Acquired in the hospital while treating other illness
- Mostly acquired by patients under long-term health care such as dialysis
- Aspiration pneumonia: Acquired due to accidental passage of a large amount of material in the lungs through mouth or stomach
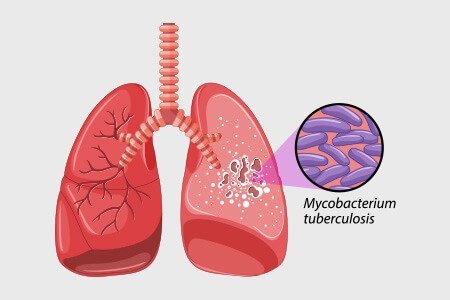
- Tuberculosis (TB): A potentially serious infection that affects the lungs. This infection can be passed from one person to another. It is of two types:
- Latent TB: The bacteria remain confined to the individual patient and does not spread to others
- Active TB: Transmission of the bacteria to others is highly likely
- Bronchitis




 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More