Bariatric Surgery
Weight loss surgery for obesity and coexisting diseases
What is bariatric surgery and who needs it?
The word ’bariatric’ is derived from the Greek words “baros” meaning “weight” and “iatrikos” meaning “medicine”. Bariatric surgery is a surgical procedure of the digestive system to promote weight-loss in people with severe obesity.
Weight-loss surgery is recommended to severely obese patients (Body Mass Index [BMI] above 40), when other weight-reduction strategies, such as diet management, exercise etc, have failed. It is also suggested in severely obese patients who have medical conditions like arthritic joint diseases that restrict the physical activity.
How does bariatric surgery work?
Bariatric surgery is a weight loss tool that influences the anatomy and hormones of the stomach and digestive system. These changes reduce hunger, emotional eating, and increase satiety, thus regularize food intake and promote fat burning. Over a period of time, the physiological changes related to energy balance and fat metabolism occur, which in turn helps to achieve a steady, desired body weight.
Thus, contrary to dietary weight loss which is usually short living and reversible, surgical weight loss offers long-lasting weight loss, improved coexisting diseases, better quality of life, improved self-esteem and psychosocial status.
Most of the bariatric surgeries are done using minimal invasive techniques such as laparoscopy.



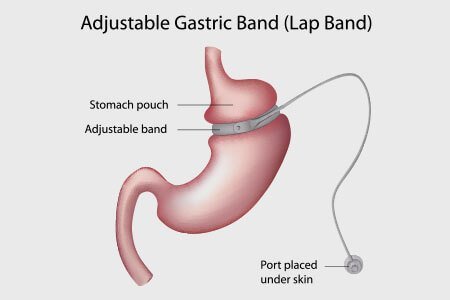
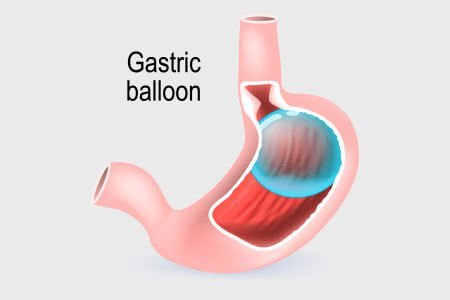
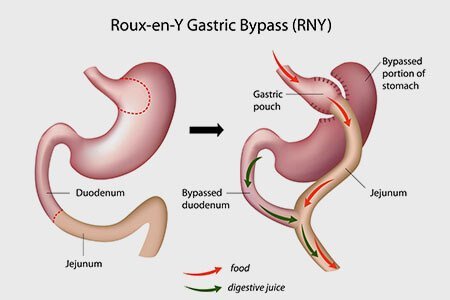
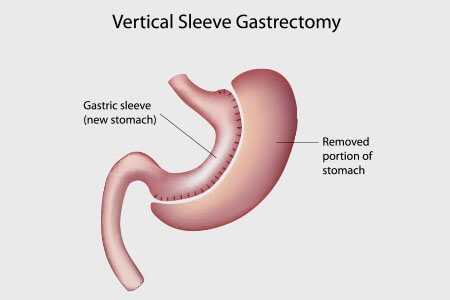

 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More

