Atrial Fibrillation & Atrial Flutter
Symptoms, types, causes, diagnosis, treatment and prevention
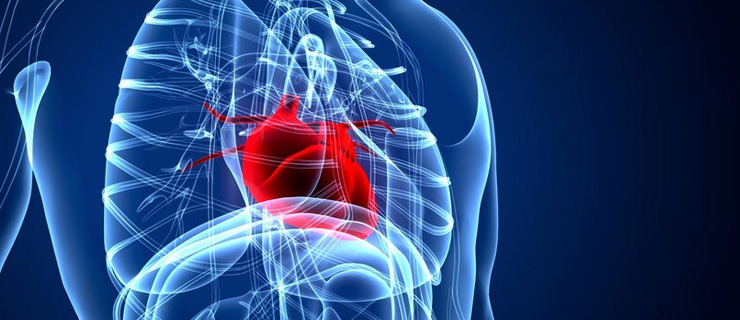
Things you need to know about Atrial fibrillation
What is atrial fibrillation?
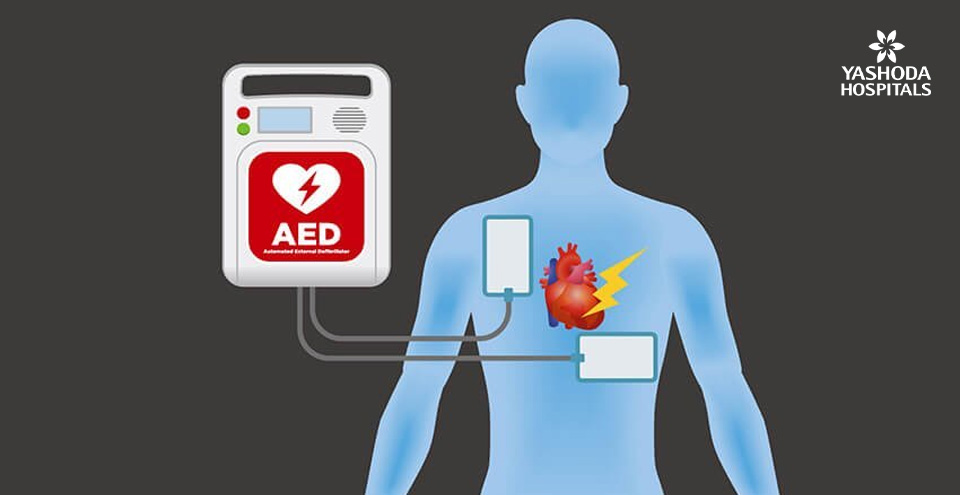
The heart is made up of four chambers, two upper “atria” and the two lower “ventricles”. The heart beats in a rhythmic pattern due to triggering of electrical impulses generated in a bunch of nerve cells called sinoartial (SA) node located in the atrium. These impulses travel to the atrioventricular (AV) node located in the ventricle. An irregular and frequently rapid heart rate is called atrial fibrillation. It occurs due to chaotic electrical signals in the atria, so they quiver. Thus impulses are bombarded to the ventricles and they also may start to beat rapidly, a sign that differentiates atrial fibrillation from flutter. As a result, the heart rhythm becomes fast and irregular. In atrial fibrillation, the heart beat may range from 100 to 175 beats a minute as compared to the normal 60 to 100 beats a minute.




 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More