Arrhythmias or irregular heartbeats
Its types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatments
What is heart arrhythmia?
The human heart is made of four sacs or chambers. The upper two are known as atria and the lower two as ventricles. A normal heart beats at a rate of 60 to 100 times per minute to circulate blood. The normal rhythm or beating of the heart is controlled by two distinct bunches of nerve cells called the Sino-Atrial (SA) node and the Atrioventricular (AV) node.
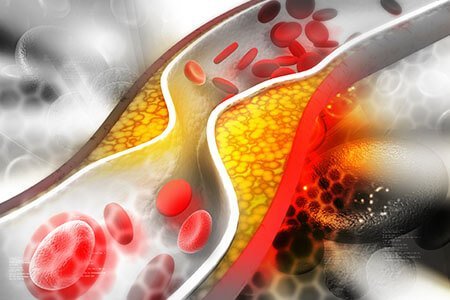
Arrhythmias, sometimes known as dysrhythmias, are disorders of electrical impulses causing the heart to beat irregularly or too fast/slow.








 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More