Osteomalacia
Causes, Symptoms, Complications, Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment
What would you like to know?
What is Osteomalacia?
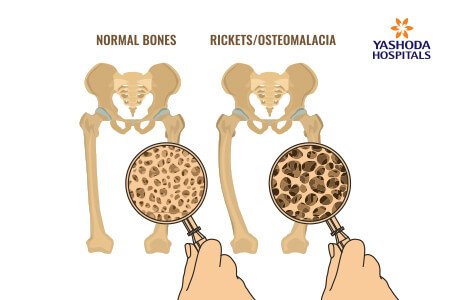
Osteomalacia is a disease condition which is characterized by softening of the bones. It is most common in children and young adults due to insufficient vitamin D levels in the body. It may also lead to bowing and fractures in individuals.
What are the causes of Osteomalacia?
Few major causes may lead to the development of osteomalacia in individuals. They are:
- Inadequate absorption of calcium from the intestine due to insufficient calcium concentrations in the diet
- Deficiency of vitamin D in the body due to lack of absorption or resistance to its action
- Deficiency of phosphate levels in the body
- Surgeries involving the stomach may hinder the absorption of vitamin D from the intestine
- Celiac disease: It is an autoimmune condition in which the consumption of foods containing gluten damages intestinal lining thereby hindering the absorption of vitamin D.
- Disorders of the liver or kidney: These organs are responsible for the activation of vitamin D in the body.
- Drugs such as antiepileptics can deplete the levels of vitamin D in the body
You may also interested in reading
Read More Information
References:
- Osteomalacia. Mayo Clinic. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/osteomalacia/symptoms-causes/syc-20355514 Accessed on June 29, 2020.
- Osteomalacia. Healthline. Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/osteomalacia Accessed on June 29, 2020.
- Osteomalacia. Versus Arthritis. Available at: https://www.versusarthritis.org/about-arthritis/conditions/osteomalacia/ Accessed on June 29, 2020.
- Osteomalacia. Cleveland Clinic. Available at: A https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/13017-osteomalacia Accessed on June 29, 2020.
Disclaimer:
“The content of this publication has been developed by a third party content providerwho are clinicians and/or medical writers and/or experts. The information contained herein is for educational purpose only and we request you to please consult a Registered Medical Practitioner or Doctor before deciding the appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan.”



 Appointment
Appointment Second Opinion
Second Opinion WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More





