Breast Cancer: What it is & How is it Treated?
Early detection and treatment gives best outcomes
Things you need to know about Breast Cancer
What is breast cancer?
As the name suggests, cancer that develops in the cells of the breast is called breast cancer (tumour). It is one of the most commonly occurring cancers in women. Over the period of last few years, advanced medical facilities have helped in early detection and treatment of breast cancer, overall reducing breast cancer related deaths.
Breast cysts are non cancerous lumps found in one or both the breasts. They are common and occur naturally due to changes in breast with aging and hormonal changes.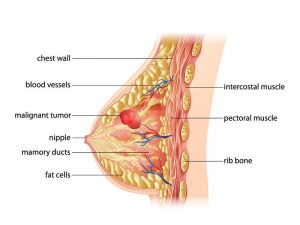
What are the types of breast cancer?
Doctors say, breast cancer occurs due to rapid, uncontrolled cell division in cells. Based on the tissues they affect, breast cancer can be:
Ductal carcinoma: cancer of milk producing ducts
Lobular carcinoma: cancer of gland tissue
Invasive breast carcinoma: When the above mentioned breast carcinoma spreads to surrounding tissues, they are called as invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma.
Metastatic breast cancer: Breast cancer may spread through blood or lymph to distant organs, this process is called as Metastasis. Metastatic breast cancer may spread to organs such as bones, lungs, liver, heart, and brain.
Male breast cancer: In rare cases, breast cancer may be diagnosed in men. Male breast cancer is usually as a result of certain medicines or abnormal hormone (estrogen) levels or strong family history of breast cancer.
Other less common types of breast cancer include medullary carcinoma, mucinous carcinoma, papillary carcinoma, inflammatory carcinoma, and phyllode tumors.
What are the causes of breast cancer?
Causes of breast cancer may be:
- Hormonal
- Hereditary or family history
- Inflammation
- Lifestyle
- Environmental triggers
What are the symptoms of breast cancer?
Some commonly seen signs and symptoms of breast cancer are:
- A thickening or a lump within the breast, which feels different from the neighbouring tissue
- A change in the shape, size or appearance of the breast
- Dimpling or pitting of the skin of the breast, making it appear like an orange peel
- Inverted nipple, which was earlier not inverted
- Dark pigmentation or flaking and peeling of skin around the nipple or anywhere on the breast
- Change in colour of the breast skin like redness
When should you consult a doctor?
In case you observe any of the above symptoms or have a doubt, visit your doctor immediately. Your doctor may refer you to an oncologist, if required.
Who is more prone to develop breast cancer?
Presence of some factors may increase the risk of breast cancer. Some of such factors are:
- Women, especially those who had their first child after 30 years of age
- Older age
- Overweight/obesity
- Past medical history of breast conditions or cancer in one of the breast
- A case of breast cancer in family, such as sister,mother or daughter, particularly at a young age
- Women on post-menopausal hormone therapy
- Prolonged exposure to radiations
- Early start of period (at younger age) or late age at menopause (ending of period)
- Excessive alcohol intake
- Genetic factors: certain gene mutations called BRCA1 and BRCA2 have been linked with breast cancer
Can breast cancer be prevented?
Breast cancer awareness can save many lives. There are several aspects of life that we can control to reduce the risk of breast cancer. Some of the precautions are listed below:
- Seek your doctor’s opinion about screening for breast cancer.
- Familiarizeyourself with the structure of your breast and regularly do a breast self-examination. It may not prevent the disease but can definitely help in early detection and management.
- Be regular for breast cancer screening as advised by your doctor.
- Quit smoking and alcohol intake.
- Engage in regular exerciseand maintain a healthy weight.
- Discuss your risk factors with your oncologist. Depending upon your risk factors, the oncologist may advice preventive medications or surgery, if required.
What are the four stages of breast cancer?
Like other cancers, pathophysiology of breast cancer progresses through 4 stages. Sooner the diagnosis, better is the treatment approach and faster is the recovery.
Based on the tumor location, involvement in the lymph nodes and spreading, TNM (tumor, node, metastasis) staging of tumor is performed. By staging the cancer, your doctor gets a better idea as to –
- Where the tumor is located exactly?
- Is the tumor spreading (also called as tumor metastases), if so, spread to lymph nodes?
- What is the prognosis for the patient – chances of complete recovery and survival?
Breast cancer may or not involve hormonal involvement – estrogen, progesterone, and HER2. Based on the status of hormones and TNM, doctor diagnoses breast cancer stages either as:
Stage 0 – Cancer at this stage is still at the origin of DNA error.
Stage 1 – Here, the cancer is confined to a limited area.
Stage 2 – In stage 2, breast cancer has begun to grow and spread through lymph nodes.
The treatment usually involves surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy (treatment after surgery aimed at trying to destroy any remaining cancer cells with or without radiation therapy).
Stage 3 – Stage 3A cancer marks the spread of cancer into the lymph nodes, the gateway to move into different parts of the body. Through stage 3B and 3C, the cancer progressively spreads through more number of lymph nodes and invades the nearby tissues but not far away organs. Treatment options are similar to that of stage 2.
Stage 4 – At this stage, cancer has spread to at least one distant part of the body – such as liver, lungs. The last stage 4B marks the spread of cancer into more than one part of the body.
What is breast cancer survival rate?
Once a person is diagnosed with cancer, the immediate question that comes to mind is, “what are my chances of survival?”
Survival rate is an estimate that can guide you if you can live through a few years. The percentage of survival rates indicate how many people have lived at least so far after diagnosis. For example, a 5-year survival rate of 90% indicates 9 in 10 cancer patients lived for a minimum 5 years after being diagnosed.
5-year survival rates for brest cancer :
|
5-year survival rate |
Stage 1 |
Stage 2 |
Stage 3 |
Stage 4 |
|
Breast Cancer |
100% |
93% |
72% |
22% |
As mentioned before, the survival rate is just an estimate and applies only in general circumstances. Discuss with your doctor to better understand your situation and to receive individualized prognosis.
There have been exceptions of people living beyond these estimated years with prompt treatment, care and support.
How is breast cancer diagnosed?
In case of any sign or symptom, visit your doctor immediately, who may refer you to an oncologist, if required. The oncologist can diagnose breast cancer by:
- Undertaking thorough medical history
- Physical examination of both the breasts and also check for swelling or hardening of any lymph nodes in the armpit
- Imaging tests:
- Mammogram: X-ray of the breast
- Ultrasound of breast
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of breast
- Tissue biopsy : Removal of the tissue of the breast for examination by a pathologist.
- Sentinel node biopsy: Once breast cancer is confirmed, patients regularly undergo sentinel node biopsy. This helps to detect cancerous cells inlymph nodes to confirm metastasis of breast cancer into lymphatic system.
If required, your oncologist may also order additional tests or procedures.
Here you can create the content that will be used within the module. Background Background: Admin Label Admin Label: How is breast cancer diagnosed? This will change the label of the module in the builder for easy identification.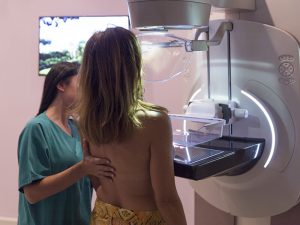
How is breast cancer treated?
The treatment options for breast cancer are based on the type and stage of breast cancer and other factors like overall health, age, and sensitivity to certain medications. The treatment options include conservative management and surgery, or a combination of both.
The conservative approaches include:
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Hormone blocking therapy
- Targeted therapy drugs
Surgical approach for breast cancer depends on the location and stage of breast cancer, as well as the risk factors in a particular patient. The oncologist/oncosurgeon will suggest the best approach, which includes:
- Mastectomy (removal of the entire breast)
- Axillary lymph node dissection (removal of several lymph nodes)
- Lumpectomy (localised removal of the breast cancer)
To know more about breast cancer and its treatment, you can request for a call back and our cancer specialist will call you and answer all your queries.
Our informative blog on Cancer:
- What is the rehabilitation for cancer patients after chemotherapy?
- Lymphoma is a group of blood cancers that develop in the lymphatic system
- If you have a lump in your neck, it could be thyroid cancer
- Prostate Cancer
- Pain during urination, frequent urination, or feeling the need to urinate could be a sign of bladder cancer
References:
- Cleveland Clinic. Total Knee Replacement. Available at:https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/total-knee-replacement-surgery Accessed on January 18, 2018.
- Royal National Hospital, NHS. A Patient’s Guide to Total Knee Replacement. Available at:https://www.rnoh.nhs.uk/sites/default/files/patient/10-85_rnoh_pg_tkr_web.pdf. Accessed on January 18, 2018.
- American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons. Total Knee Replacement. Available at:https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/treatment/total-knee-replacement. Accessed on January 18, 2018.
- US National Library of Medicine, Medline Plus. Knee Replacement. Available at: https://medlineplus.gov/kneereplacement.html. Accessed on January 18, 2018.



 Appointment
Appointment Second Opinion
Second Opinion WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More





