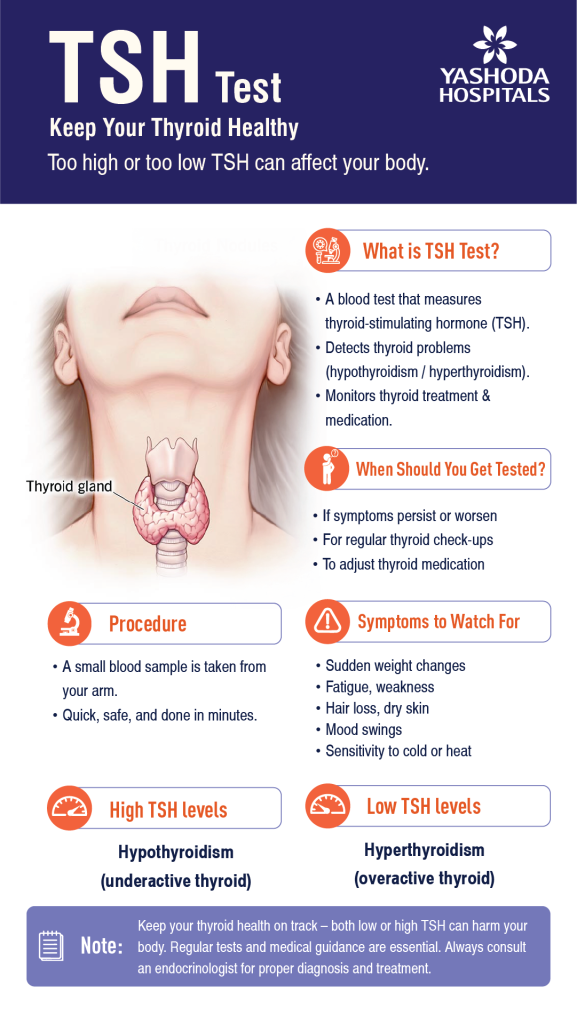
What is the Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Test?
A thyroid-stimulating hormone test (TSH) evaluates the level of thyroid hormone in the blood via a blood test. The thyroid gland has a butterfly shape and is located near the throat, which synthesizes hormones that determine the body’s metabolism, development, and growth.
One of the brain’s glands, named the pituitary, synthesizes the TSH. The TSH and thyroid levels are inversely proportional. That is, when the thyroid level is low, the pituitary gland secretes more TSH. An overactive thyroid gland results in hyperthyroidism, and an underactive thyroid gland results in hypothyroidism. Further, the TSH test is also known as thyrotropin and thyrotropin hormone test.




 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More