Yellow Lies: Decoding The Myths About Jaundice
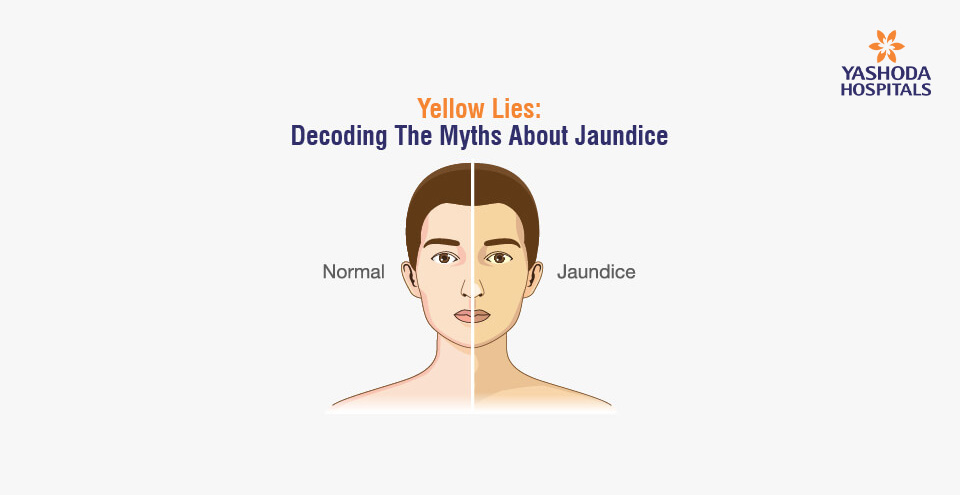
Jaundice is a yellowing of the skin and eyes caused by an excess of bilirubin in the body. Bilirubin, the yellow pigment produced during the breakdown of red blood cells, is normally processed by the liver and excreted in the bile. Impaired liver function is the most common cause of jaundice.
This condition is characterised by yellowing of the skin and eyes, dark urine, pale stools, and itching that can be caused by a number of conditions, including liver disease, gallstones, and certain medications. It may also be brought on by an underlying medical condition, such as cancer or an infection.
It is a common condition that affects many people, but there is a lot of misinformation out there about it. In this blog, we will explore the myths and facts about jaundice, so you can make informed decisions about your health. So let’s get started!
Common Myths and Facts About Jaundice
Myth 1: Jaundice is contagious.
Fact: No, jaundice itself is not contagious. Jaundice is caused by an excess of bilirubin in the bloodstream and is a symptom of an underlying medical condition such as liver disease.
However, the underlying medical condition that causes jaundice can be contagious. For example, hepatitis A, B, and C are all contagious viral infections that can cause jaundice. Other contagious illnesses that can cause jaundice include mononucleosis, malaria, and cytomegalovirus. Furthermore, some newborns develop jaundice as a result of an immature liver, which is not contagious.
Myth 2: Jaundice is always serious.
Fact: While jaundice can be a sign of a serious medical condition, it is not always serious. In some cases, jaundice can be caused by a minor infection or other benign condition, while in other cases it may be a sign of a more serious medical condition such as liver disease, gallstones, or cancer.
However, if you or someone you know is experiencing jaundice, it is critical to seek medical attention because it can be a sign of a serious medical condition that requires treatment.
Jaundice presents with symptoms such as yellowing of the skin and eyes, dark urine, pale stools, and itchy skin.
Myth 3: Jaundice patients should only consume bland, boiled foods.
While bland, boiled foods may be easier to digest, jaundice patients should also consume a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
When a person has jaundice, their body is unable to process and eliminate toxins as efficiently as it normally would. As a result, it is important for jaundice patients to consume foods that are low in fat, high in carbohydrates, and easy to digest.
Myth 4: Jaundice is caused by eating too much junk or fatty food.
Fact: Jaundice is not caused by consuming an excessive amount of junk or fatty food. It is a condition caused by an excess of the yellow pigment bilirubin in the blood, which is produced by the breakdown of red blood cells. It can be caused by a number of conditions, including liver disease, certain medications, and infections.
However, eating a diet high in unhealthy foods can result in other health problems, like obesity, which increases the risk of developing jaundice.
Myth 5: Consuming alcohol with food does not result in jaundice.
Fact: While alcohol consumption with food does not directly cause jaundice, it can be a contributing factor. Alcohol can damage the liver, the organ responsible for breaking down and eliminating toxins from the body. When the liver is damaged, it can lead to a buildup of toxins in the body, which can cause jaundice.
Additionally, alcohol can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb certain vitamins and minerals, which can also lead to jaundice.
Myth 6: Jaundice can be cured with home remedies.
Fact: Jaundice cannot be cured with home remedies. Although home remedies can help relieve some of the symptoms of jaundice, such as fatigue, nausea, and itching, they cannot cure the condition.
If you suspect you have jaundice, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. Your doctor will be able to diagnose the condition and provide the appropriate treatment.
Myth 7: It is safe to drink alcohol immediately after recovering from jaundice.

Fact: Alcohol consumption can impair the body’s ability to process bilirubin, exacerbating the jaundice. It can also interfere with the body’s ability to absorb nutrients, which can further weaken the body and delay recovery. Therefore, it is important to refrain from consuming alcohol until the jaundice has been treated completely.
Furthermore, after recovery, it is critical to consume alcohol in moderation and with caution, as alcohol can have a negative impact on the body even after the jaundice has been treated. Hence, it is crucial to drink responsibly and be aware of any potential risks related to alcohol use.
In conclusion, jaundice is a common condition that can affect newborns and adults alike. While there are many myths surrounding jaundice, it is important to understand the facts in order to properly diagnose and treat the condition. With proper medical care, jaundice can be managed and treated effectively.
References:
- Is Jaundice Contagious?
https://www.healthline.com/health/is-jaundice-contagious - Adult Jaundice
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases - Everything you need to know about jaundice
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/165749 - Jaundice in Adults
https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/quick-facts-liver-and-gallbladder-disorders
About Author –
Dr. Adi Rakesh Kumar, Consultant Gastroenterologist,Therapeutic Endoscopist & Endosonologist, Yashoda Hospitals, Secunderabad
M.B.B.S, M.D., DM (Gastroenterology)
















 Appointment
Appointment Second Opinion
Second Opinion WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More





