A thick, waxy plaque can limit, or completely obstruct, blood flow to the brain
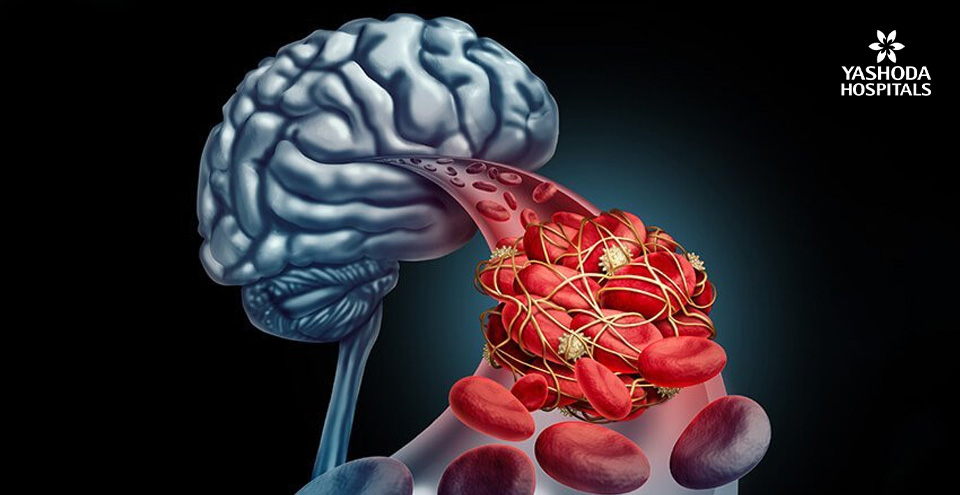
What is Cerebrovascular Disease?
The term ÷ cerebrovascular’s consists of two parts cerebro is a large part of the brain and vascular includes arteries and veins. It refers to a set of circumstances that cause hindrance to the circulation of blood to the brain, resulting in limited or less flow of blood to the affected portions of the brain.
On most of the occasions, people with a history of smoking, diabetes or heart diseases tend to be affected by cerebrovascular disease. Approximately, 1.2-.2.5 out of every 1000 children is affected by the disease.
Symptoms
The symptoms of cerebrovascular disease are triggered by the area of the patient’s hemorrhage, embolism or thrombus, besides the extent to which the cerebral tissue has been impacted. The symptoms include:
- Motor dysfunction
- Abrupt change in the patient’s face such as inability to smile, drooping of the eye or the mouth
- Vomiting
- Slurring of speech
- Fever
- Seizures(Fits)
- Abnormalities in ECG
- Difficulty in breathing
- Progressive decline in speech
- Headache on one side of the head
- Neck pain
Causes
Cerebrovascular disease is impacted by certain medications, lack of nutrients, tumors in the brain. This disease is caused by atherosclerosis, a condition in which excess cholesterol and arterial inflammation in the brain cause the cholesterol to store into a thick, waxy plaque that can cause block the flow of blood to the train, resulting in transient ischemic attack or ischemic stroke.
Risk Factors and Complications
In the inception stages of the disease, the patient suffers flaccid paralysis, spasticity and enhanced muscle tone. Further, the patient may face communication problems like dysphagia, expressive aphasia or receptive, apraxia and dysarthria, besides losing the ability to cough, loss of half of the visual field and inability to identify an object.
The other major risk factors are:
- Hypertension
- B.P.
- Uninhibited Diabetes
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Ethnicity
Tests and Diagnosis
The following diagnostic imaging tests facilitate best neurosurgeon in hyderabad to examine the arteries and vessels surrounding the brain and brain tissue thereby determining the disease:
- Cerebral angiography: This helps in knowing about blockages in the blood vessels of your neck and head. The procedure involves using a catheter, a long and flexible tube along with an external X-ray to obtain detailed images of these vessels.
- Carotid-artery duplex: This is an ultrasound scan test that is noninvasive and painless. The purpose of this test is to determine the blood flow of the arteries that transmit from the heart through the neck to the brain. It is also done to hear any abnormal sound in carotid arteries (neck) with the help of a stethoscope.
- Computed Tomography (CT scan): In this test, a medication will be given through a vein to help expose brain structures. Brain, blood and bone tissues are all easily identifiable on a CT scan.
- Electroencephalogram: By way of keeping electrodes on the patient’s scalp, the electrical activity of the brain is measured.
- Lumbar Puncture: It is an invasive diagnostic imaging test that is useful in recognizing bleeding impacted by a cerebral hemorrhage. As part of the test, a needle is used to take out a sample of cerebrospinal fluid from the space nearby the spinal cord.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging: This test generates three-dimensional images of body structures with the help of magnetic fields and computer technology. Different types of nerve tissue and vivid pictures of the posterior brain and the brain stem and signs of pre mini-strokes get surfaced in the test.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiogram: Through MRA test, the magnetic images are put together by a computer to get images of the arteries in your neck and head. This test aids in detecting blockage and aneurysms, in addition to displaying the real blood vessels in the brain and neck.
Treatment
Treatment methods for cerebrovascular disease are dependent on the patient’s characteristics such as age, the nature and severity of the specific disease.
Further, there are both surgical and non-surgical treatment methods available to tackle the disease.
Medications (blood platelet inhibitors) like dipyiridamole, aspirin, ticlopidine, sulfinpyrazone and clopidogrel will prove to be effective in dealing with the risk for stroke.
There are a variety of surgical procedures such as:
- Surgical resection
- Carotid angioplasty and stenting
- Surgical aneurysm repair
- Endovascular embolization
- Interventional neuroendovascular surgery
- Stereotactic radio surgery















 Appointment
Appointment Second Opinion
Second Opinion WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More





