Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis Successfully Maintained on Rituximab Biosimilar for Five Years
Background
A 52 years old Indian female was referred from a hospital to us because of a cough persisting for three months, shortness of breath, right sided chest pain, occasional fever, sleeplessness, loss of appetite and generalised weakness.
Examination
Chest examination revealed scattered crepitations on auscultation of the lungs bilaterally. Heart sounds were normal. No fourth heart sound or rub was heard. The abdomen was symmetrical without distention bowel sounds were normal in quality and intensity in all areas. No masses or splenomegaly were noted; the liver span was 8cm by percussion. CNS examination was normal.
Diagnosis
Chest radiograph revealed a multi lobulated mass in the right mid zone of the lungs the impression was probably cancer. It was followed up by High Resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT) chest which confirmed the presence of right lower apical segment mass and multiple well defined nodules seen in the right upper lobe, right middle lobe, lingual and left lower lobe.
The patient underwent bronchoscopy and bronchial sputum/smear specimens were negative for bacteria, Acid Fast Bacilli (AFB), fungal elements and malignant cells.
The patient then underwent CT guided biopsies which showed necro inflammatory debris without any evidence of granuloma/malignant cells/fungal elements. Tumour markers (CEA, CA, 19, 9 & CA 125) were negative. Blood tests and serology confirmed Anti neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (C ANCA) was positive with anti PR3>200. C Reactive Protein (CRP) (96), Rheumatoid factor (640) and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) (140mm/hr) were elevated. Anti-Nuclear Antibody (ANA) was negative. Urine examination revealed microscopic haematuria (10 15 RBC/HPF) with mild proteinuria (Spot urine for protein creatinine ratio 0.96).
Treatment
The patient was started on pulse therapy of methyl prednisolone for five days followed by cyclophosphamide and steroids for six cycles. However, despite this, the patient’s condition progressively worsened with increasing breathlessness, severe debilitating joint pains, headache and generalised weakness. Patient also developed sudden loss of vision due to retrobulbar optic neuritis which was treated by IV methyl prednisolone.
Due to refractoriness of the disease to the conventional treatment, and the progressive worsening of symptoms, Rituximab Biosimilar 1g followed by a second infusion two weeks later was given. After this, her ESR dropped to 40mm/hr and urine examination became normal.
Follow up Chest X ray revealed fibrosis in the right mid zone with the rest of the lung parenchyma appearing normal. Anti PR3 antibodies were 0.24 and her clinical course seemed to have stabilised. BVAS WG score reduced to 1.
After induction doses of Rituximab Biosimilar, she received 1g infusion every six months for the next four years as maintenance. A low dose of steroids was continued all throughout. She was clinically stable for the entire period, with no major flare ups.
Almost a year after 10 Rituximab infusions, she has remained well and in remission. She responded very well to the treatment with Rituximab Biosimilar symptomatically and as evidenced by her blood reports.
Rituximab is a chimeric monoclonal anti CD20 antibody mainly used for the treatment of B cell lymphomas. It has recently been used as a salvage therapy in the treatment of various refractory autoimmune diseases. It can be assumed that Rituximab is a safe and efficacious alternative for patients with GPA. It has shown minimal side effects.
This case report emphasizes that contrary to current literature this treatment can be safely continued for over five years in whom conventional immunosuppressive agents have failed or have contraindications to its use.
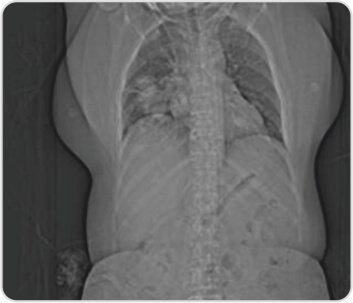
CT topogram of the chest reveals right lower lobe consolidation
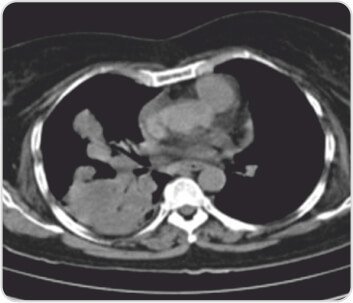
CT scan of chest showingRight lower and middle lobe consolidation
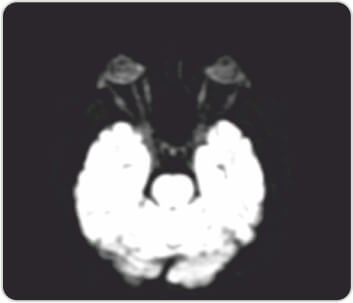
Right optic nerve showsincrease in a signal due to optic neuritis
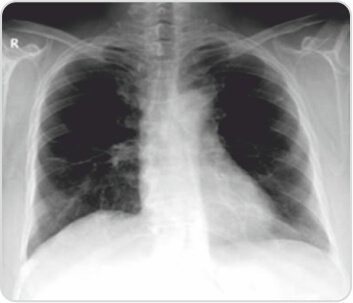
Post treatment chest radiograph showingcomplete resolution of right lower lobe consolidation with few fibrotic strands seen at the site of involvement in the right mid zone








 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More