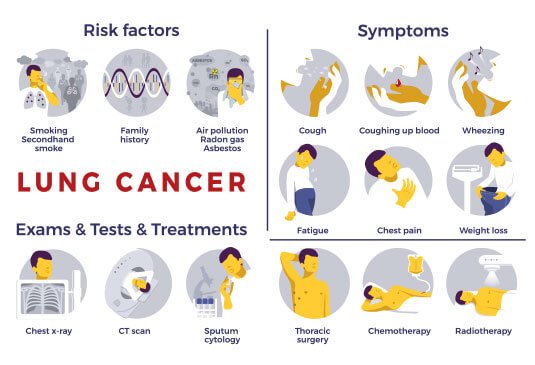
Diagnosis of lung cancer
In addition to a medical history and examination that may be indicative of lung cancer, the doctor may order certain tests as mentioned below to look for cancerous cells and to rule out other conditions.
- Imaging tests: Tests like an X-ray image of the lungs that may reveal the presence of an abnormal mass or nodule. Sometimes smaller lesions that are not distinctly visible in the X-ray can be detected in a CT scan.
- Sputum cytology: A microscopic examination of the phlegm or sputum produced during coughing may reveal the presence of abnormal cancer cells.
- Biopsy: Removal of a sample of abnormal cells is done in a procedure called a biopsy. For the detection of lung cancer, bronchoscopy, mediastinoscopy, or needle biopsy are the methods by which a sample of the suspected tissue is obtained.
Imaging procedures help in determining the extent of spread of cancer beyond the lungs. These tests may include include CT, MRI, positron emission tomography (PET) and bone scans. However, they may not be indicated in every case. So, it is always recommended to talk with the treating doctor to decide the most appropriate tests.
Patient Testimonials For Cancer











 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More

