Brain injury or traumatic brain injury
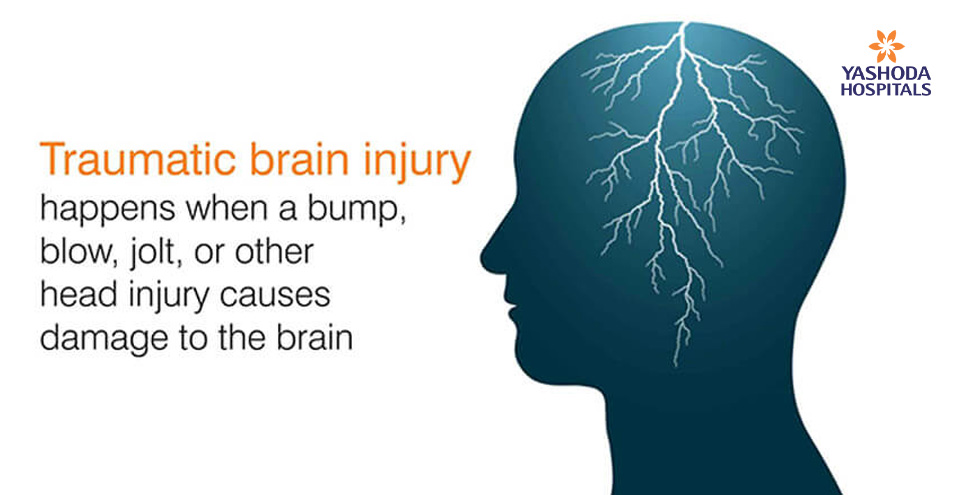
Traumatic brain injury happens when a bump, blow, jolt, or other head injury causes damage to the brain.
Brain injury or traumatic brain injury is caused by brain dysfunction following an external force or violent blow. Brain injury may also occur when a foreign object penetrates the skull. The skull is damaged with something like a bullet, sharp material and stone penetrates the skull to cause traumatic brain injury. The fall-out of brain injury is seen as temporary dysfunction of brain cells, bruising, torn tissues, bleeding, physical damage and long-term complications or death.
CAUSES
Several factors may cause traumatic brain injury. The attending doctor or neurologist may suggest treatment depending on the degree of the damage to the brain. Traumatic brain injury may occur due to,
Damage to brain cells due to sudden impact or fall on the head; Rotational or spinning jolt leading to tearing of cellular structures; Explosion due to bomb or other factors that causes excessive damage to the skull and the brain; Swelling and blood clots disrupt oxygen supply leading to brain damage; and vehicle-related accidents can result in severe head injuries, trauma and bleeding.
RISK FACTORS AND COMPLICATIONS
Three age groups are greatly susceptible to traumatic brain injury – Just born to 4 year olds, young adults between 15 and 24, and seniors who are 75 and older. The complications of more severe head injuries are evident as coma, vegetative state, minimally conscious state, locked-in syndrome, and brain death.
In some the traumatic brain injury is evident as, seizures, fluid buildup, infections, blood vessel damage, nerve damage (paralysis) and intellectual problems (loss of memory). There is also greater risk of having degenerative brain diseases in those suffering from traumatic brain injuries. These include Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and Dementia pugilistica.
TESTS AND DIAGNOSIS
Traumatic brain injury, in majority of the cases is an emergency. The attending medical personnel or the doctor checks the patient’s condition and severity of the injury by applying the Glasgow Coma Scale. Answers are sought to be found for questions such as, how the injury occurred/happened; Is the injured conscious or unconscious; Since how long is the injured unconscious; What are the changes in alertness, speaking and coordination in the injured; Was the head alone or other parts of the body were affected by the accident; and Information about the force of the injury.
After receiving the needful clarification on the above questions, few tests such as computerized tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are done on immediate basis. To study the tissue swelling inside the brain, the doctors my probe through the skull to monitor this pressure.
TREATMENTS AND DRUGS
The mild trauma brain injuries need no treatment. Taking rest and pain relievers constitute the usual course of treatment for mild trauma brain injuries. However, when it is a case of severe traumatic brain injury, immediate emergency care needs to be provided to the aggrieved. This includes, providing oxygen and blood supply, and maintaining blood pressure helps in preventing further injury to the neck or head.
In the Intensive Care Unit or Emergency Room, the treatment is done for inflammation, excess bleeding and reduced oxygen supply to the brain. The surgery includes, removing the clotted blood, repairing skull fractures, and creating an opening in the skull to reduce pressure inside the skull, and draining it of cerebral spinal fluids.















 Appointment
Appointment Second Opinion
Second Opinion WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More





