Understanding Radiation Oncology in Cancer Treatment
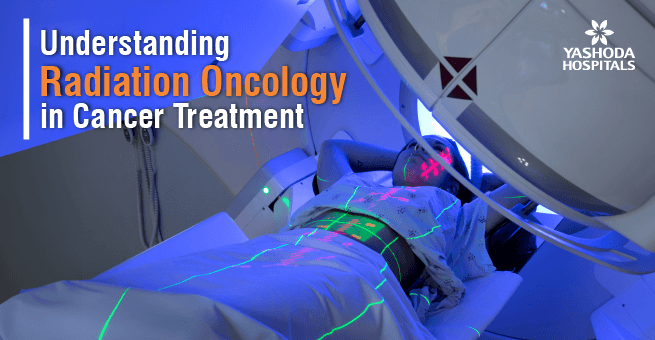
Cancer remains one of the most challenging health issues worldwide, with millions of lives affected each year. As medical science advances, so does the arsenal of tools available to combat this formidable foe. One such powerful weapon to fight against cancer is Radiation Oncology, a specialized branch of medicine dedicated to using targeted radiation to treat tumors. Now let’s explore the intricacies of Radiation Oncology, its various types, and its distinct advantages over other treatment modalities.
Understanding Radiation Oncology
Radiation Oncology, also known as Radiation Therapy, is a medical discipline that utilizes high doses of radiation to kill or damage cancer cells. The primary goal is to shrink tumors and eliminate cancer cells, either as the main form of treatment or in conjunction with surgery and chemotherapy. Unlike chemotherapy, which involves the use of drugs to target cancer cells throughout the body, radiation therapy precisely targets specific areas affected by tumors.
Types of Radiation Therapy
- External Beam Radiation: This is the most common form of radiation therapy. It involves directing high-energy beams from an external machine towards the cancerous tumor. The process is painless, and patients do not become radioactive during or after treatment.
- Internal Radiation (Brachytherapy): In this method, a radioactive source is placed inside or very close to the tumor. This allows for a highly targeted delivery of radiation while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissues. Brachytherapy is commonly used in the treatment of prostate, breast, and cervical cancers.

- Targeted Radiation Therapy: This cutting-edge approach involves using specialized drugs that specifically target cancer cells, making them more sensitive to radiation. By combining targeted drugs with radiation therapy, healthcare providers can enhance the effectiveness of treatment while reducing damage to normal, healthy cells.
- Linac Radiotherapy (Linear Accelerator): Linear accelerators, commonly known as linacs, are sophisticated machines that generate high-energy X-rays or electrons to treat cancer. Linac therapy is a type of external beam radiation therapy that delivers precise and controlled doses of radiation to the tumor. This technology allows for the customization of treatment angles and intensities, ensuring accuracy in targeting cancer cells while sparing adjacent healthy tissues.
Radiation Therapy Procedure
The radiation therapy procedure is a carefully planned and executed process that involves several key steps:
- Simulation: Before treatment begins, a simulation session is conducted to map the treatment area precisely. This often involves the use of imaging techniques such as CT scans or MRI to identify the tumor’s location and determine the optimal angles for delivering radiation.
- Treatment Planning: Oncologists, medical physicists, and dosimetrists collaborate to create a detailed treatment plan based on the simulation data. This plan outlines the dosage, duration, and angles of radiation delivery to maximize its impact on cancer cells while minimizing harm to healthy tissues.
- Treatment Delivery: With the plan in place, patients undergo the actual radiation therapy sessions. The radiation machine is carefully calibrated to deliver the prescribed dose with precision. Patients may need multiple sessions over a specified period, depending on the type and stage of cancer.
- Monitoring and Adjustments: Throughout the treatment course, medical professionals closely monitor patients to assess their response and manage any potential side effects. Adjustments to the treatment plan may be made if necessary to ensure optimal outcomes.
- Follow-up Care: After completing the radiation therapy course, patients undergo regular follow-up appointments to monitor their recovery and address any lingering side effects. Follow-up imaging and tests help healthcare providers assess the treatment’s success and make further recommendations for ongoing care.
Radiotherapy VS Chemotherapy
- Precision vs. Systemic: Radiation therapy is a localized treatment that precisely targets the affected area, minimizing damage to healthy tissues. Chemotherapy, on the other hand, is a systemic treatment that circulates throughout the body, affecting both cancerous and healthy cells.
- Side Effects: Radiation therapy tends to have fewer systemic side effects compared to chemotherapy, as it primarily affects the targeted area. However, both treatments can cause side effects, and the severity depends on factors such as the type of cancer, the location of the tumor, and the patient’s overall health.

Safety and Benefits of Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is a highly controlled and safe treatment modality when administered by trained professionals. Here are some key benefits and safety considerations:
- Precise Targeting: Advanced imaging technologies, such as CT scans and MRI, help oncologists precisely locate and target tumors, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
- Pain Management: Radiation therapy is effective in relieving pain associated with certain cancers, such as bone metastases.
- Combination Therapy: Radiation therapy can be used in combination with surgery and chemotherapy to enhance treatment outcomes, providing a multi-modal approach to cancer care.
- Personalized Treatment: Each patient’s treatment plan is tailored to their specific cancer type, stage, and individual health profile, ensuring a personalized and effective approach.

Radiation Oncology plays a crucial role in the comprehensive treatment of cancer, offering a targeted and effective means of eliminating tumors while minimizing damage to healthy tissues. As technology continues to advance, the field of Radiation Oncology holds promise for even more precise and personalized cancer treatments. This powerful tool, alongside surgery and chemotherapy, provides patients with hope and an increased chance of successful cancer management and recovery.
Are you aware that smoking causes irreversible lung damage, contributing to 7 million deaths annually worldwide?
Frequently Asked Questions:
- Can Radiation Cause Cancer?
Controlled and targeted radiation therapy used in cancer treatment poses a minimal risk of causing new cancers. The therapeutic benefits typically outweigh potential long-term effects.
- Can cancerous cells be easily destroyed by radiation?
Yes, radiation destroys cancer cells by damaging their DNA, targeting the tumor with precision. Success depends on factors like cancer type and stage, often used alongside other treatments.
- What are the indications for radiation therapy?
Indications for radiation therapy include primary treatment for certain cancers, adjuvant therapy post-surgery to eliminate remaining cancer cells, palliative care for symptom alleviation in advanced cases, and preoperative treatment to shrink tumors before surgery.
- Best Radiation therapy treatment in Hyderabad?
Yashoda Hospitals, Hyderabad is renowned for providing top-notch radiation therapy treatment, ensuring advanced and comprehensive care for cancer patients.
References:
- Understanding Radiation Oncology: https://www.mayoclinic.org/departments-centers/radiation-oncology/sections/overview/ovc-2018
- Types of Radiation:https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/types/radiation-therapy
- Linac Radiotherapy https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/linac
- Radiotherapy VS Chemotherapy https://treatcancer.com/blog/difference-chemotherapy-radiation/
- Safety and Benefits of Radiation Therapy
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/managing-cancer/treatment-types/radiation/safety.html#
About Author –
















 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More