Spyglass Cholangioscopy

What are Gallstones?
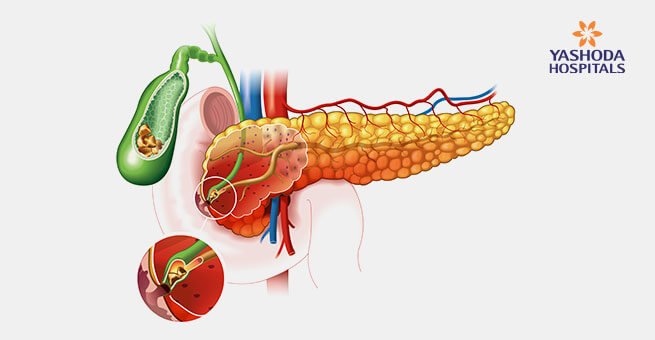
Gallstones are the solid concretions varying in different sizes and shapes. These are formed in the gallbladder and appear to be the hardened deposits of the digestive fluid. Gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ which is located on the right side of the abdomen beneath the liver. A digestive fluid called bile is present in the gallbladder that is released into the small intestine.
What are the different types of Gallstones?
There are two main types of gallstones:
- Cholesterol stones: These are yellow-green in colour and are most common constituting upto 80% of gallstones.
- Pigment stones: These are made of bilirubin and are small and dark.
What are the risk factors for Gallstones?
There are a various factors that increase the risk of developing gallstones such as:
- Sex: When compared to men, gallstones are observed more common in women.
- Age: As the age increases, the risk of developing gallstones also increases.
- Family history and genetics: Gallstones are developed commonly in certain families reflecting the effect of genetics in the gallstone development.
- Other factors: Other conditions such as obesity, pregnancy, sudden weight loss, diabetes mellitus, frequent fasting, lack of physical activity can increase the risk of developing gallstones.

What are the symptoms of Gallstones?
Usually, gallstones present no signs or symptoms. If a gallstone causes a blockage in the duct, the resulting signs and symptoms may include:
- Back pain between the shoulder blades
- Sudden intense pain in the upper right portion and center of the abdomen
- Pain in the right shoulder
- Nausea or vomiting
The pain caused due to gallstone formation may last for several minutes to a few hours.
Sudden Acute abdominal pain is the most common initial symptom of gallstones. Often located in the right upper belly just under the lower ribs. Sometimes this pain can be misleading to a heart attack. But the majority of people who have gallstones do not present any symptoms and their stones remain “silent.”
What are the complications of Gallstones?
The complications associated with gallstones may include:
- Cholecystitis: This is a condition where inflammation is observed in gallbladder due to the lodging of gallstone in the neck of the gallbladder. Severe pain and fever are also observed.
- Common bile duct blockage: A blockage can occur in the bile duct due to accumulation of gallstones through which bile flows from the gallbladder or liver to the small intestine. It can result in bile duct infection, severe pain, and jaundice.
- Pancreatic duct blockage: The pancreatic duct is a tube like structure that runs from the pancreas connecting the common bile duct before entering the duodenum.
- Pancreatitis: Due to blockage of pancreatic duct by gallstone can lead to inflammation of the pancreas. Pancreatitis causes constant, intense abdominal pain and usually requires hospitalization.
- Gallbladder cancer: People with a history of gallstones have an increased risk of gallbladder cancer.
What is Spyglass Cholangioscopy?
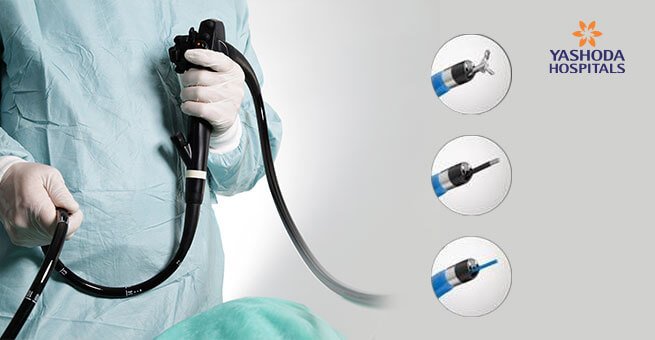
Spyglass Cholangioscopy is a novel technique developed for the visualization of bile ducts. It allows the doctor to observe the biliary duct system along with the small pancreatic ducts which are difficult to reach. It consists of a 6,000-pixel, fiber-optic probe which is attached to a tiny camera.
The procedure can be performed by an endoscopist. In the SpyGlass system, the endoscopes were fragile and difficult to use. The newer versions of the SpyScope provide better and easier visualization. The Spyscope is the endoscope used in SpyGlass cholangioscopy.
Many people undergo Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) procedures to diagnose and treat diseases and conditions of the gallbladder, liver, pancreas, and bile ducts. Spyglass cholangioscopy aids in the direct examination of the bile ducts using a spyglass scope. This small caliber scope is inserted into the bile duct or pancreatic duct to enable the direct visualization during ERCP. It also helps to obtain biopsy specimens. This technology provides additional information beyond the standard fluoroscopic (x-ray) examination of the bile ducts and pancreatic ducts normally obtained during ERCP.
The small Spyglass scope is attached to the larger endoscope used for ERCP procedure. The Spyscope is composed of a lighted camera, an irrigation system and a suction to flush and clean out the debris. Additionally, the Spyscope has a working channel with a laser to break up stones and forceps for tissue sampling during biopsies.
Spyglass is a highly advanced and valuable tool used as an extension to standard ERCP. It enables the physician to diagnose and treat pancreatic and biliary diseases more efficiently and effectively.
How Spyglass Cholangioscopy is used in treating Gallstones?
For such large stones stuck in Bile duct, they can now be removed endoscopically using the latest “Spyglass Cholangioscopy” which is like baby scopy which enters the bile duct and by using the latest laser we can break the stones and successfully clear the bile duct without surgery. Since this is a day care procedure, the patient can go back home on the same day of the procedure.
References
- Spyglass Cholangioscopy, Medscape, https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1891395-technique. Accessed on 1st November 2020.
- What Is SpyGlass Cholangioscopy?, MedicineNet, https://www.medicinenet.com/what_is_spyglass_cholangioscopy/article.htm. Accessed on 1st November 2020
- Spyglass Cholangioscopy, University of South Florida, https://health.usf.edu/medicine/internalmedicine/digestive/spyglass. Accessed on 1st November 2020
- Gallstones, WebMD, https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gallstones/symptoms-causes/syc-20354214. Accessed on 1st November 2020
About Author –
Dr. Adi Rakesh Kumar, Consultant Gastroenterologist,Therapeutic Endoscopist & Endosonologist, Yashoda Hospitals, Secunderabad
M.B.B.S, M.D., DM (Gastroenterology)















 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More