At a Glance:
1. What is simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation?
2. Who is eligible for pancreas-kidney transplantation?
3. What are the benefits of pancreas-kidney transplantation?
4. What are the risks of pancreas-kidney transplantation?
5. Is a type-2 diabetes patient eligible for pancreas-kidney transplantation?
6. Can the kidney and pancreas be transplanted separately?
7. What is the survival rate of pancreas-kidney transplantation?
8. What is the evaluation for pancreas-kidney transplantation?
9. What happens during the pancreas-kidney transplantation?
10. What happens after pancreas-kidney transplantation surgery?
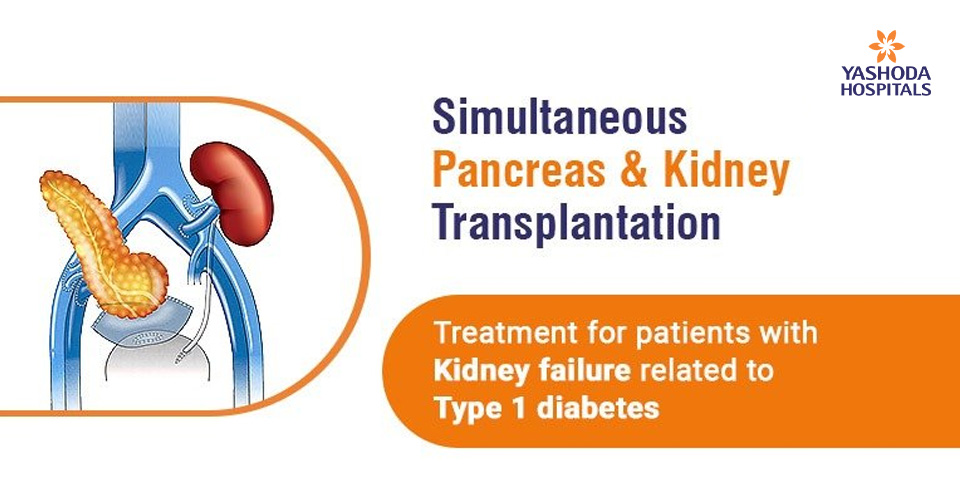
What is simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation?
Simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation is the best treatment for diabetic patients with failing kidneys due to the onset of diabetic nephropathy or chronic kidney disease. The primary goal is to replace the pancreas and give complete independence to the patient from injected insulin. The transplanted pancreas is fully functional in not only producing insulin to control the recipient’s blood sugar levels, but also producing enzymes to support digestion in the gut. Thus, SPK offers vastly improved quality of life (QoL) of the patient.
In SPK, the kidney and pancreas are removed from the deceased donor and given to the recipient who is fit for the operation. SPK is not a cure but is drastically beneficial in not only controlling diabetes but also replace the failing kidneys.
Simultaneous pancreas-kidney (SPK) transplantation is the most commonly performed multi-organ transplantation. This week, the team of doctors at Yashoda hospitals successfully completed the simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation on a 32 years old male with type-1 diabetes and kidney failure. The pancreas and the kidney were both harvested from a 25-year old deceased donor. The open surgery was performed over a period of 12 hours.
Who is eligible for pancreas-kidney transplantation?
Doctors may recommend pancreas transplantation if:
- Insulin-dependent with a C-peptide of 2 ng/mL or less (patients with type 1 diabetes)
- Insulin-dependent with a C-peptide greater than 2 ng/mL and a body mass index 2</sup> (presumably patients with type 2 diabetes)
In either case, the pancreas of patients does not produce enough insulin, an essential hormone that controls blood sugar in the body. The transplanted pancreas will be able to correct type-1 diabetes through the production of insulin.
Doctors may recommend simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation if:
- The patient suffers from kidney failure due to type-1 diabetes.
- They suspect the beginning of kidney failure in a patient with type-1 diabetes.
The decision will be taken by the doctor and transplantation surgeon based on the patient’s medical condition and health. A pre-transplantation evaluation will also be required, which will include a series of tests such as bladder and heart evaluations.
What are the benefits of pancreas-kidney transplantation?
A successful simultaneous kidney and pancreas transplantation improves quality of life so the individual may:
- Have increased stamina and strength for daily activities.
- Have improved sex life and fertility, especially for women in child-bearing age.
- Better blood sugar control without the need of insulin and constant monitoring
- Have a healthy diet with normal levels of fluid intake.
- Eliminate the need for dialysis.
- Have normal blood sugar levels before and after eating.
Benefits of combined pancreas-kidney transplantation are related to vascular complications related to blood supply, heart diseases etc. Patients experience stabilized or improved complications:
- Diabetic nephropathy and kidney failure
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Coronary artery disease
- Stroke
- Neuropathy
What are the risks of pancreas-kidney transplantation?
Due to the transplantation of two organs in the body, the risks associated with the procedure are higher than those associated with single organ transplantation. They may be:
- Rejection of organs: Any transplantation surgery will be associated with the risk of the body rejecting the newly transplanted organs. The patient will have to take anti-rejection medications for life to prevent rejection.
- Primary non-function and pancreas failure: In 5-10% of the cases, the nonfunctional pancreas may have to be removed within the first year of transplantation.
- Delayed kidney function: This may require dialysis until kidneys begin to work
- Dehydration after surgery
- Infection and blood loss
Is a type-2 diabetes patient eligible for pancreas-kidney transplantation?
A person with type-2 diabetes can be eligible for simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation, though this happens very rarely. Generally, the transplanted pancreas does not work effectively for type-2 diabetes patients. The doctor and transplantation surgeon may still opt for the procedure due to the unique circumstances and health conditions of the patient. Thus, it is best to consult a healthcare professional regarding the evaluation of eligibility.
Can the kidney and pancreas be transplanted separately?
This is possible. In some cases, the patient with kidney failure related to type-1 diabetes may first get kidney transplantation due to various factors. This is later followed by the pancreas transplantation.
Can the patient have pancreas transplantation without kidney transplantation?
Based on the patient’s condition, the doctor may go for only pancreas transplantation, omitting the kidney transplantation. This may happen if the patient:
- Already had a kidney transplantation
- Shows the complications associated with type-1 diabetes but does not have kidney failure.
What is the survival rate of pancreas-kidney transplantation?
After the transplantation, the survival rate of adults is 92.5% three years later. The best results are seen when the pancreas and kidney come from the same donor i.e. a deceased donor. This decreases the chances of the body rejecting the transplant organs. In the case of a living donor, if the kidney comes from a closely matched donor (a relative or sibling), then the success rate is better than if the organs come from a less closely matched donor.
Increasingly, SPK transplantations have been done recently with a living donor, wherein a kidney and a segment of the pancreas are donated.
What is the evaluation for pancreas-kidney transplantation?
The patient is evaluated by a group of stakeholders, including a transplant surgeon and a nephrologist (kidney doctor). They will record the patient’s medical history, conduct a physical exam, and request the following tests (among many):
- Blood tests
- Neurological tests
- Tests to confirm type -1 diabetes
- Tests to check heart and lung function
- Test to evaluate kidneys
Depending on the results of the tests, the patient will be accepted for pancreas-kidney transplantation. They will be placed on the transplant center’s waiting list. The process to search for a living donor may also begin.
What happens during the pancreas-kidney transplantation?
During the operation, the healthy kidney and pancreas are placed into the body to replace the failing functions of the original organs. The original kidneys and pancreas are generally not removed, and the kidney is placed in the left side of the lower abdomen while the pancreas is placed in the right side of the same region.
The surgery lasts anywhere between 4 to 12 hours. The patient may have to stay in the hospital for 2 to 4 weeks after that. The pancreas begins to produce insulin within a few hours after the surgery. Insulin shots will not be required from this point onward.
What happens after pancreas-kidney transplantation surgery?
The procedure followed after the operation depends on the patient’s reaction to the transplantations. It is generally as follows:
- The first few days of the postoperative stage will be spent in the ICU, where the patient is closely monitored to ensure the good functioning of the pancreas and kidney.
- Provided that there is no rejection (of the organs) or infection, the patient will be discharged in a span of 7-10 days.
- The patient will be required to take anti-rejection medications for the rest of their life to prevent their body from rejecting the transplant organs.
- There will be regular follow-ups with the doctor to ensure the healthy functioning of the transplanted organs.
- The patient will be expected to have a healthy lifestyle.
Conclusion:
The advantages of simultaneous pancreas-kidney (SPK) transplantation is becoming obvious with improved surgical outcomes and diabetes control. SPK transplantation is the first alternative to insulin therapy for insulin-dependent diabetes patients. Other alternatives include pancreas transplantation alone (PTA), islet-cell transplantation. SPK is not a cure but drastically beneficial in not only controlling diabetes but also replace the failing kidneys. SPK is a major surgery which comes with certain risks and complications. Talk to your doctor for more information.
References:
- Thomas, Beje. “Kidney-Pancreas Transplantation”. Edited by Ron Shapiro. Medscape. Accessed on 16 August 2019. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1830202-overview
- “Kidney-Pancreas Transplant”. National Kidney Foundation. Accessed on 16 August 2018. https://www.kidney.org/atoz/content/kidpantx
- Having a simultaneous pancreas-kidney (SPK) transplant. NHS. Accessed on 16 August 2019. https://www.guysandstthomas.nhs.uk/resources/patient-information/kidney/having-a-simultaneous-pancreas-kidney-(spk)-transplant.pdf
Recent Posts
రక్తదానం: అర్హులు, ప్రయోజనాలు మరియు అపోహల గురించి సంక్షిప్త సమాచారం
మనిషి బ్రతకడానికి ప్రాణవాయువు ఆక్సిజన్ ఎంత అవసరమో రక్తం కూడా అంతే అవసరం. రక్తం, శరీరంలోని ప్రతి కణంతో అనుక్షణం…
నరాల సంబంధిత వ్యాధుల రకాలు, కారణాలు, లక్షణాలు & నిర్ధారణ పరీక్షలు
నరాల సంబంధిత రుగ్మతలు అంటే నాడీ వ్యవస్థ మొత్తం మీద ప్రభావం చూపే వ్యాధులు. నాడీ సంబంధిత పరిస్థితులు ఇప్పుడు…
Endovascular Surgery: Minimally Invasive Solution to Vascular Disease
Endovascular surgery is a revolutionary advancement in medical technology wherein doctors can treat almost any…
పల్మోనరీ ఎంబోలిజం: లక్షణాలు, కారణాలు మరియు చికిత్స విధానాలు
పల్మోనరీ ఎంబోలిజం అనేది చికిత్స మీద ఆధారపడిన ఒక తీవ్రమైన పరిస్థితి, ఇది సాధారణంగా ఊపిరితిత్తులకు ప్రయాణించే రక్తంలో గడ్డకట్టడం…
Rhinoplasty: Understanding the Nose Surgery Procedure and Its Benefits
Rhinoplasty is commonly known as a nose job that is usually designed to reshape a…
Is Spine Surgery Safe? Exploring Minimally Invasive Techniques and Recovery
Spine surgery is a source of fear for most people, yet it has undergone significant…