Hypothyroidism is a common disorder of the endocrine system
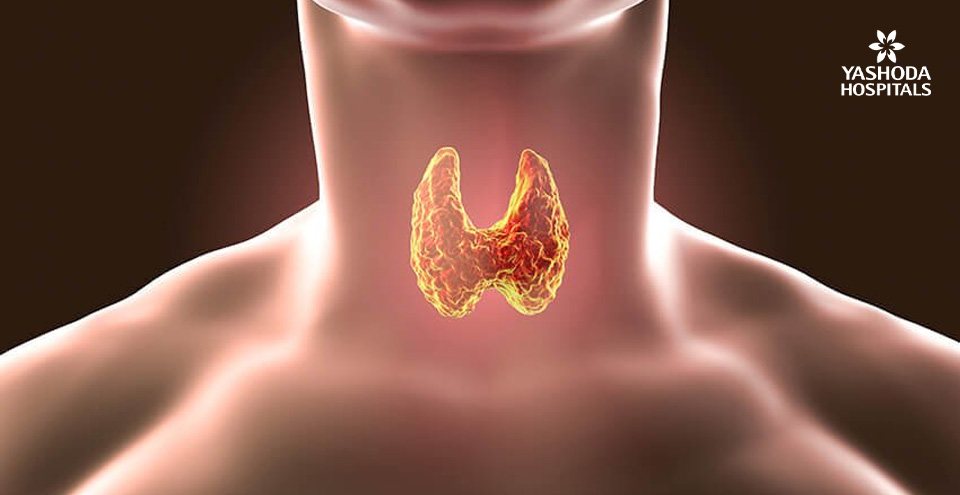
Hypothyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. Thyroid is a small gland present at the base and front of the neck, below the Adam’s apple. Thyroid gland produces two types of hormones, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), which help in controlling metabolism of the body (body temperature, heart rate, and regulation of the production of proteins.
Women more than 60 are more likely to develop this condition. If left untreated, hypothyroidism causes obesity, joint pain, infertility and heart disease. The synthetic thyroid hormone is administered to the patient under the supervision of a doctor or endocrinologist.

CAUSES
The causes for hyperthyroidism are autoimmune disease, hyperthyroidism, radiation therapy, thyroid surgery and certain medications. Autoimmune disorders produce antibodies that attack the body’s tissues.
Reaction caused by medication may also cause hypothyroidism. People with excess production of thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism) are treated with radioactive iodine or anti-thyroid medications, which may sometimes result in hypothyroidism.
Significantly, iodine deficiency can also cause hypothyroidism. The trace mineral iodine is present in seafood, seaweed, and plants grown in iodine-rich soils. However, taking too much of iodine viz iodized salt may result in hypothyroidism.
SYMPTOMS
Depending on the severity of thyroid deficiency the symptoms may become evident. At the early stage, the symptoms of hypothyroidism are barely visible. It takes a few years for the symptoms to become clear. Fatigue and weight gain are commonly seen in people with hypothyroidism.
Other symptoms of thyroid are evident as sensitivity to cold, constipation, dry skin, puffy face, hoarse voice, muscle weakness, rise in blood cholesterol, pain and stiffness in the joints, regular or irregular menstrual periods, hair thinning, slower heart rate, depression and impaired memory.
Myxedema is the advanced form of hypothyroidism. During myxedema the patient suffers from low blood pressure, decreased breathing, decreased body temperature, unresponsiveness and even coma.
Hypothyroidism may also occur in infants. The symptoms include, yellowing of the skin, frequent choking, protruding tongue, puffy face, constipation, and excessive sleepiness.
RISK FACTORS & COMPLICATIONS
If left untreated, hypothyroidism may have a disastrous fall-out on human health. In pregnant women, it may result in birth of babies with mental and physical development issues. It may also affect ovulation and decrease chances of conceiving. In some, it may lead to heart disease due to increased levels of “bad” cholesterol. There is also gradual decrease in mental functioning and increase in depression.
TESTS AND DIAGNOSIS
The diagnosis of underactive thyroid condition or hypothyroidism includes blood tests that measure the level of TSH, and the level of thyroxine, the thyroid hormone. TSH test is advancement over other blood tests, as it helps in identifying thyroid condition even before symptoms are experienced.
TREATMENT
A synthetic thyroid hormone taken on a daily basis is the standard treatment for hypothyroidism. To determine the right dosage of synthetic thyroid hormone, the level of TSH is checked every two to three months.
Read more about thyroid problems, symptoms, causes and treatment.
















 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More