How to diagnose and treat Myelodysplastic Syndrome?
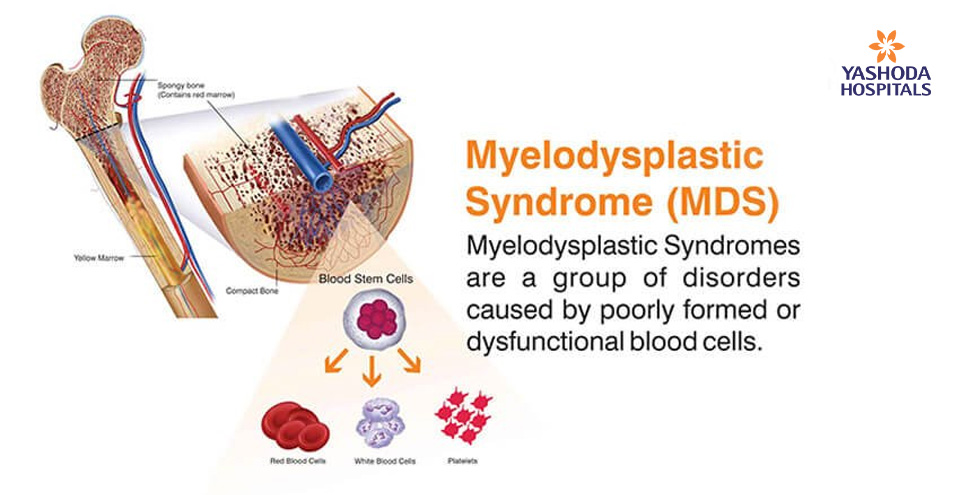
Myelodysplastic Syndrome is a condition where the bone marrow fails to produce proper number of blood cells (RBC, WBC and Platelets). In the last stages, Myelodysplastic syndrome may turn into acute myeloid leukemia, a type of cancer. People with myelodysplastic syndrome have immature and defective blood cells that lead to problems of anemia, infections and excess bleeding.
CAUSES
The exact causes of myelodysplastic syndrome are not known. However, chemicals and radiation which are part of cancer treatment may have a fall-out that is evident as Myelodysplastic syndrome.
SYMPTOMS
In the early stages of Myelodysplastic syndrome, there are no visible symptoms. The symptoms of Myelodysplastic syndrome may include, Fatigue, Shortness of breath, Unusual paleness (pallor) due to anemia, Easy or unusual bruising or bleeding, Pinpoint-sized red spots just beneath your skin caused by bleeding (petechiae), and Frequent infections.
RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS
The risks of myelodysplastic syndrome are caused by older age, chemotherapy and radiation, exposure to chemicals and heavy metals. The complications of myelodysplastic syndrome are evident as anemia due to reduced number of red blood cells, fewer white blood cells means risk of infections, lesser platelets means excessive bleeding, and increased risk of cancer (leukemia).
TESTS AND DIAGNOSIS
The doctor prescribes different tests. The blood test helps the doctor to get the patient’ complete blood picture. The bone marrow test helps the doctor to assess the condition of the bone marrow. During this test, a small amount of the bone marrow is extracted from the patient’s bone marrow. In the lab the bone marrow is tested for abnormalities.
TREATMENTS AND DRUGS
The treatment for myelodysplastic syndrome includes blood transfusions, medications and bone marrow transplant. Blood transfusions replace old blood cells with new blood cells. There are medications that help in increasing the number of blood cells in the body. In bone marrow or stem cell transplant the abnormal bone marrow stem cells are replaced by healthy donated cells.















 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More