How to diagnose and treat Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome?
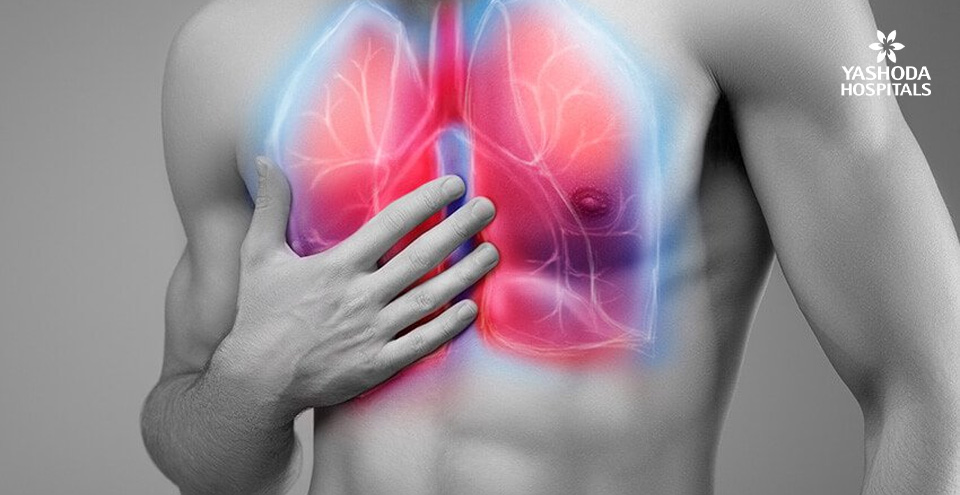
ARDS is a critical condition when there is fluid build up in the lungs:
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome is a condition where fluid collects in the lungs preventing oxygen from reaching the rest of the organs. It is a life threatening lung condition and progresses rather quickly, but is generally treatable and can be recovered from with the right care and quick treatment.
Symptoms:
The ARDS makes in very hard for the person to breathe and can put a lot of strain on the lungs, this is a primary symptom of the disease. Other symptoms include:
- Confusion
- Low blood pressure
- Quick and shallow breathing
- Sweating
- dizziness
- Organ failure
Most often than not, symptoms of ARDS set in quickly and intensely. It happens anywhere between 24 to 48 hours after an injury or trauma.
Causes and Risk Factors:
While there is a lot of research going on on the causes of ARDS, there is no concrete reason on what can trigger it. Some of the common triggers however can be an accident which can cause trauma to the body, especially the lungs. It can also be caused by injury to the brain as well, the portion that controls the breathing. ARDS can also happen if poisonous substances or vomit are inhaled into the lungs.
ARDS leads to a build up of fluid in the alveoli (air sacs) of the lungs, which prevents oxygen from being absorbed, leading to a lack of oxygen in other organs in the body. This can cause the lungs to become stiff and even heavy, making it hard for them to expand. When this happens, the level of oxygen in the body gets to a critical low and might even become fatal.
Since ARDS most often than not accompanies other illnesses, people most likely to develop ARDS include those over 65, who smoke, have a history of alcoholism or even a lung disease and toxic shock.

Tests and diagnosis:
There is no single test that can determine ARDS and often more than one test is done to determine and confirm it. Since ARDS is an emergency condition, it is important to catch it early for the best chances of survival. A drop in the level of oxygen in the body also helps in determining ARDS.
Here are some of the other tests done to determine and diagnose ARDS:
- Blood pressure
- Blood tests
- X- Ray of the chest
- C T Scan
- Airway examination
- Nose and throat swabs
Treatment:
The primary goal of ARDS is to provide the required oxygen to the body. This can be done in various ways:
- Provision of oxygen by mask: This is done by a mechanical ventillation machine that forces air into the lungs.
- Fluid management: it is essential to maintain the right amount of fluid so too much does not drown the lungs and too little does not strain the heart.
- Medication: Medication is often used to keep the person calm so the other treatment can be fully effective in its treatment.
Recovery and Prognosis:
Recovery from ARDS can be tough for some people. While a lot of people recover from ARDS, the road to recovery can sometimes take months, or even years. Side affects of ARDS can include muscle weakness and fatigue that may take the body some time to recover from. But recovery is complete with people living full and happy lives after.
Why Yashoda
The Critical Care department at Yashoda Hospitals provides the best possible intensive care treatment for people in a critical condition. Some of the many conditions that the critical care team caters to include heart conditions, nervous disorders, sepsis, shock, ARDS, etc. The infrastructure includes a CCU with the latest multipara monitors, invasive and non-invasive hemodynamic monitoring, Portable X-rays, bedside EEG ABG analysis, Echocardiography and dialysis and Gastric Tonometry.












 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More