Crohns Disease
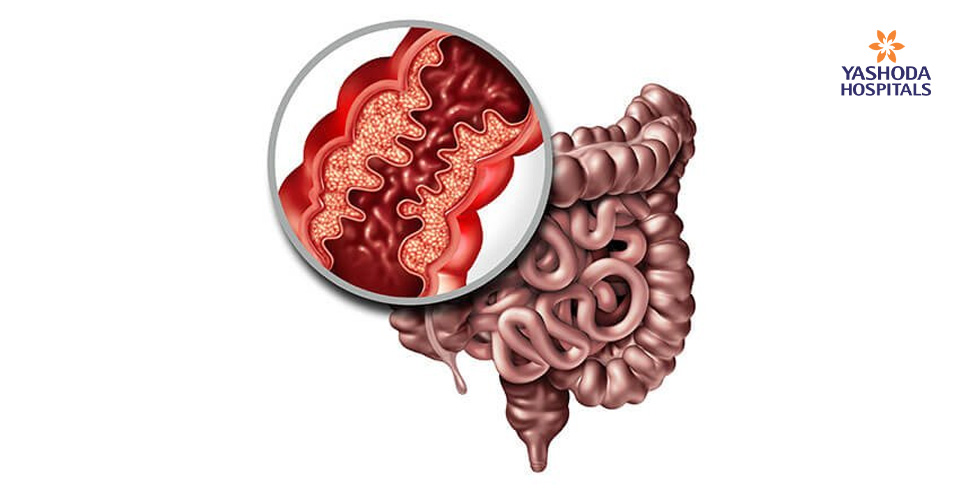
Crohn’s disease may affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from mouth to anus.
Crohn’s disease or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) affects the digestive tract. The symptoms of Crohn’s disease are evident as abdominal pain, severe diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss and malnutrition. Significantly, Crohn’s disease may spread to different areas of the digestive tract. It may be both painful and debilitating and may also lead to life-threatening condition.
CAUSES
The exact causes of Crohn’s disease are not known. Diet and stress are considered to aggravate Crohn’s disease. Significantly, hereditary and malfunctioning of the immune system are considered to cause Crohn’s disease. The body’s immune system responds to virus or bacterial attack which may also result in attacking the cells in the digestive tract. Sometimes, family history of Crohn’s disease with strong hereditary linkage may also be considered as a potential cause for Crohn’s disease.
SYMPTOMS
Those affected by Crohn’s disease may exhibit symptoms of diarrhea, fever and fatigue, abdominal pain and cramps, blood in the stool, mouth sores, reduced appetite, weight loss and perianal disease. Of all these symptoms, diarrhea, abdominal pain and cramps are commonly seen in the affected. In some, the symptoms are evident as inflammation of skin, eyes and joints; inflammation of liver or bile ducts; and delayed growth or sexual development.
RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS
Age, ethnicity, family history, cigarette smoking, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications and the environment are considered as potential risk factors for Crohn’s disease. Those who are less than 30 years old and those with a family history of Crohn’s disease are increasingly prone to Crohn’s disease. Those living in urban and industrialized areas which are highly polluted are also greatly prone to Crohn’s disease. The complications of Crohn’s disease are evident as chronic inflammation and sores (ulcers) anywhere in the digestive tract.
TESTS AND DIAGNOSIS
The doctor looks for symptoms of Crohn’s disease viz. diarrhea, fever and fatigue, abdominal pain and cramps, blood in the stool, mouth sores, reduced appetite, weight loss and perianal disease. In certain cases, the doctor may recommend for tests that include colonoscopy, flexible sigmoidoscopy, computerized tomography (CT) scan, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), capsule endoscopy, double balloon endoscopy and small bowel imaging. Each test has a specific purpose, and on case-to-case basis the doctor may advise for the specific test(s).
TREATMENT
Depending on the severity of the Crohn’s disease, the doctor may advise on the appropriate course of treatment that includes diet and lifestyle changes, drug therapy and surgery.
Know more about symptoms, causes, diagnosis, risk factors and treatment of irritable bowel disease














 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More