Compartment Syndrome can be acute (severe injury) or chronic (athletic exertion).
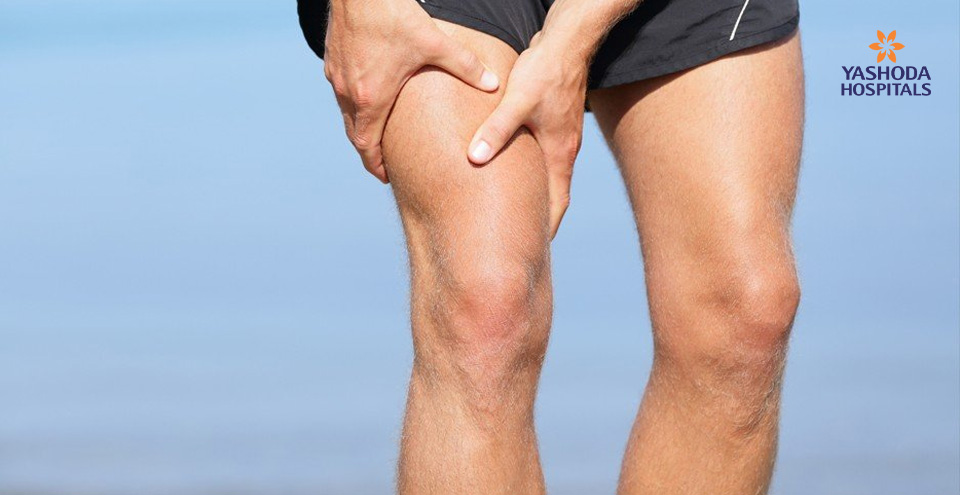
Compartment Syndrome is a condition wherein pressure builds up inside the human body in any of its enclosed spaces. This condition may arise due to swelling or bleeding post an injury. Frequently, it occurs in spaces in the leg or arm. Compartment syndrome may be acute or chronic.
In India, abdominal compartment syndrome occurs in about 50% general surgical or trauma patients getting intensive care, yet it is poorly understood and under diagnosed.
Symptoms
People with acute compartment syndrome have the following symptoms:
- Pain not in proportion with the injury
- A sensation of pins and needles in the affected area
- Paralysis of the affected limb
- Swollen, tense, shiny skin
In chronic compartment syndrome, the pain in the affected limb worsens within 30 minutes of doing physical exercise. Symptoms are relieved with stress.
Causes
Acute compartment syndrome may be caused by a fracture, or by the pressure from the bleeding and swelling. It may also be caused by treatment of the fracture, say by casting or surgery.
Injuries without the bone may also cause acute compartment syndrome, for instance:
- Very tight bandaging
- Blood clot in blood vessel of arm or leg
- Burns
- Crush injuries
- Surgery in blood vessel of arm or leg
Risk factors and complications
Below factors put people at risk of developing chronic compartment syndrome:
- Athletes below the age of 40 years
- Exercising with repetitive motions or activity
- Playing football and tennis, running, cycling, and participating in gymnastics
- Too much training
Complications of acute compartment syndrome include tissue necrosis within 12 hours and muscle necrosis. Chronic acute compartment syndrome makes the patient more likely to suffer from acute compartment syndrome.
Test and Diagnosis
Compartment syndrome can be detected by orthopedic hospitals in Hyderabad by directly measuring the pressure inside the body compartment.
- A needle is inserted into the body compartment.
- An attached pressure monitor measures the pressure inside the body space.
- Doctors may also insert a plastic catheter to continuously monitor the pressure inside the compartment.
When abdominal compartment syndrome is suspected, a urinary catheter is used to insert a pressure monitor into the bladder.
- If high pressures are observed in the bladder, it is almost certain that the condition is abdominal compartment syndrome.
To support the diagnosis of compartment syndrome, laboratory tests and imaging techniques are used. However, the most conclusive test is a direct measurement of pressure.
Treatment
To treat acute compartment syndrome, immediate surgery is required to reduce the pressure in the enclosed body space.
- The affected body part is elevated so that blood flow is improved.
- Oxygen is given through the nose or mouth
- Pain medication is given.
- Fluids are provided intravenously.
For chronic compartment syndrome, the first step is to avoid the activity that causes the condition. Next, physical exercises and stretching should be done.
If surgery is necessary to reduce the extra pressure, your doctor may recommend it.
Abdominal compartment syndrome requires the following treatments:
- Mechanical ventilation
- Blood pressure medication
- Kidney replacement therapy (e.g. dialysis)
Compartment syndrome can be fatal if not diagnosed on time and treated appropriately.
















 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More