Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Chronic kidney disease or chronic kidney failure is a slow and progressive loss of kidney function over a period of several years
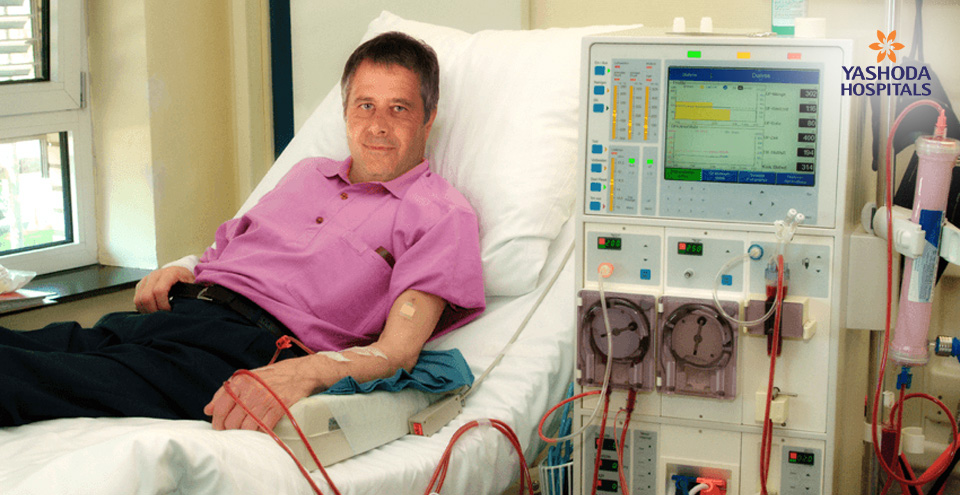
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) also described as chronic kidney failure is a condition where kidneys gradually stop functioning. The primary function of kidneys is to filter wastes and excess fluids from the blood. In the advanced stage of chronic kidney disease, the fluids, electrolytes and wastes build-up in the body. This condition may require artificial filtering (dialysis) or kidney transplant.
CAUSES
Not one cause but multiple causes result in chronic kidney disease. These include, Type 1 & 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, glomerulonephritis (inflammation of kidney’s tubules and surrounding structures, polycystic kidney disease, prolonged obstruction of the urinary tract, Vesicoureteral reflux (reverse flow of urine to kidneys) and pyelonephritis (recurrent kidney infection).

SYMPTOMS
The symptoms of kidney disease include, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fatigue and weakness, sleep problems, decreased mental sharpness, muscle cramps, swelling of feet, persistent itching, shortness of breath and high blood pressure. The symptoms of kidney diseases may not appear till the condition reaches an advanced stage.
RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS
The risk of chronic kidney disease is enhanced by diabetes, high blood pressure, cardio-vascular diseases, smoking, obesity and family history of kidney diseases. The complications of chronic kidney disease are evident as swelling of arms and legs due to fluid retention, rise in potassium levels in the blood, increased risk of bone cancers, erectile dysfunction, nerve damage and difficulty to concentrate, decreased immunity, pregnancy problems and kidney damage.
TESTS AND DIAGNOSIS
The doctor may pose questions relating to your medical history, family history of kidney problems and medications. To confirm on chronic kidney disease the doctor may recommend tests of blood and urine. Imaging tests may also be advised. In some instances the doctor may insist on removing a sample of kidney tissue for testing. Blood and urine tests reveal the level of waste products (creatinine and urea) in the blood. Ultrasound helps to assess the kidneys’ structure and size. The biopsy process involves removing a sample of the kidney tissue to assess the stage of kidney disease and kidney function.
TREATMENTS
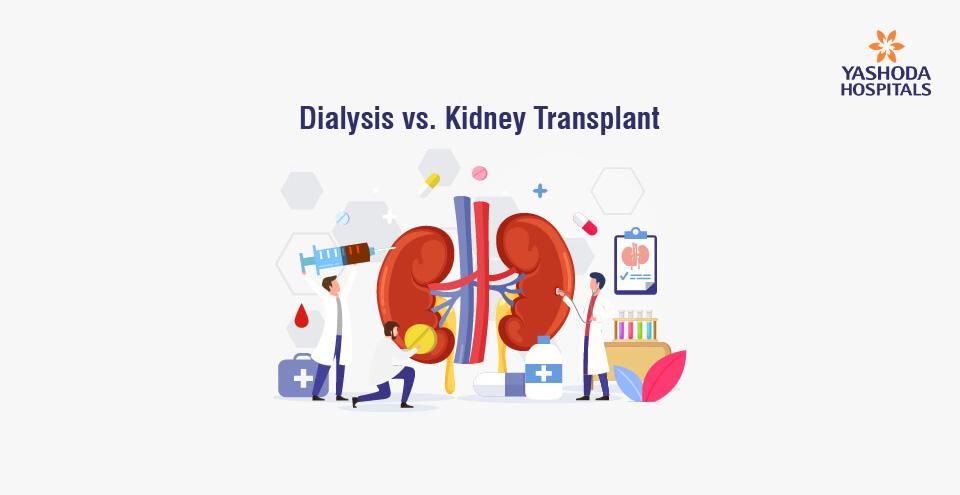
The treatment for chronic kidney disease includes efforts to control signs and symptoms, reduce complications and slowdown the disease progression. Significantly, the treatment for chronic kidney disease includes treating the underlying condition such as high blood pressure, lower cholesterol levels, anaemia, and diet control. The treatment also includes prescribing calcium and vitamin supplements for healthy bones, and medications to reduce swelling of legs. You may have to take a diet with low protein content. Intake of less protein means less work for kidneys and lower level of waste products that kidneys have to filter from your blood. For patients with end-stage kidney disease dialysis or kidney transplant may be recommended.
















 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More