Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) injury – Role of Arthroscopy
At a Glance:
What is anterior cruciate ligament?
What is (Anterior Cruciate Ligament) ACL injury?
What are the symptoms of an ACL tear?
What are the ACL injury treatments available? What are the types of ACL surgery grafts?
What is Arthroscopic ACL reconstruction surgery?
How is the arthroscopic ACL reconstruction surgery performed?
What is the recovery time for ACL reconstruction surgery?
What are the factors affecting the cost of ACL reconstruction surgery?
What is a knee joint?
Knee joint is the bony structure of the knee in the form of a hinge that connects the 3 bones namely the femur (thigh bone), tibia (leg bone), and patella (knee cap). These bones within the knee joint are held together by four cruciate ligaments namely anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL) and lateral collateral ligament (LCL).
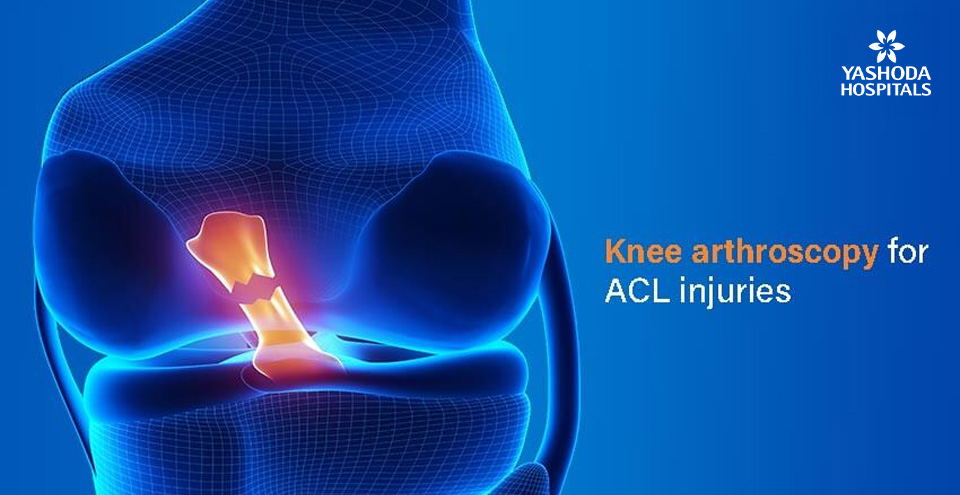
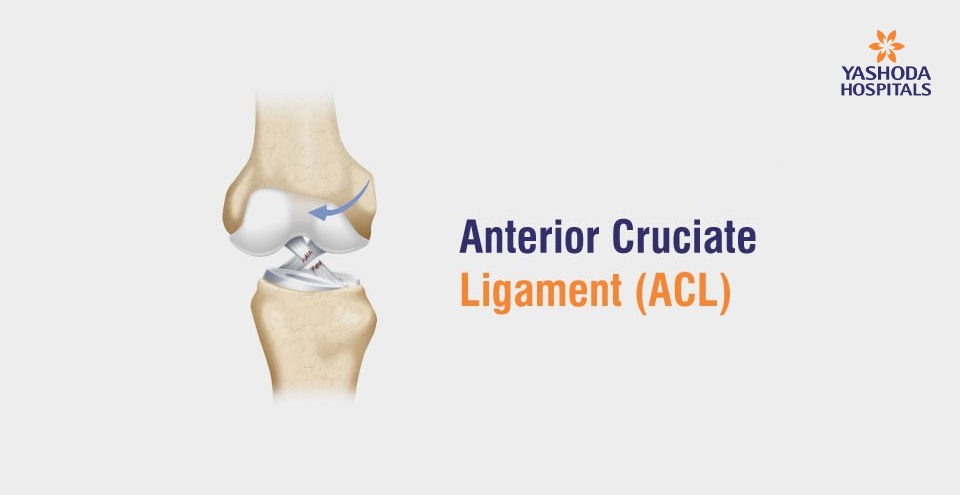
What is anterior cruciate ligament?
The ACL amongst these is the main stabilizing ligament that connects the femur to the tibia through the centre of the knee. This is one of the bands of tissue that holds the bones together within the knee. It also helps to keep the knee stable. The main function of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is to prevent the leg bone from slipping anteriorly. ACL is vital for maintaining stability in physical activities like stepping, jumping etc.
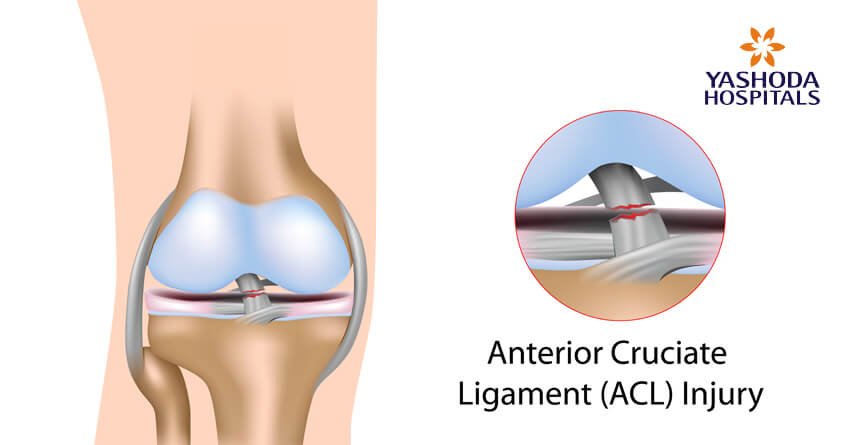
What is (Anterior Cruciate Ligament) ACL injury?
An ACL injury is a sprain or tear of the anterior cruciate ligament which is a most commonly seen sports injury in athletes and sportsperson involved in tennis, basketball, football etc.
How do ACL injuries happen?
The ACL is susceptible to injuries during intense physical activities and sports. Like, other sports injuries, some of the common reasons for ACL injuries include:
- Sudden or rapid change in direction
- Halting suddenly while walking
- Changing pace or slowing down while running
- Incorrect landing from a jump
- A direct physical blow to the knee during contact sports like football or accident
What are the symptoms of ACL tear?
Injury to the anterior cruciate ligament may be accompanied with a “popping” noise with a feeling of buckling or knee giving out from under. Some other associated symptoms include:
- Pain and swelling: After an ACL injury, the knee may start swelling within 24 hours. Sometimes the swelling and pain get resolved on its own if adequate rest is given. However in case the person continues with strenuous activity or continues with sports activity, it may lead to further instability and damage to the meniscus or the cartilage that functions as a cushion for the knee.
- Inability to perform the whole range of motions at the knee joint
- Tenderness in the joint region
- Walking becomes uncomfortable
How is an ACL injury diagnosed?
ACL injuries are usually treated by an orthopaedic surgeon. The diagnosis is done by:
A) Medical history and physical examination
The orthopaedic surgeon takes a complete medical history, details of symptoms and performs the physical examination of the knee.
B) Imaging Tests
The orthopaedic surgeon may want to confirm the diagnosis with imaging tests like:
- X-rays: To determine if the injury is associated with any broken bone. X-rays are of little clinical value in diagnosing an ACL tear.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan:The soft tissues within the knee like the anterior cruciate ligament can be studied better in MRI that may sometimes be required.
What are the treatment options for an ACL injury? What are the types of ACL surgery grafts?
The treatment for an ACL injury depends on various factors like age, medical condition and activity level of a person. As an example, in case of an ACL injury in a person who is engaged in high-intensity activities like sports may need to undergo arthroscopic ACL reconstruction procedure for early return to routine activities. The treatment options are usually:
Nonsurgical management:
Even though a torn ACL may not heal without surgical intervention, A nonsurgical treatment may be considered in elderly persons or those with very low activity level. The orthopaedic surgeon may recommend simple, nonsurgical options in persons unfit to undergo surgery or in cases where the stability of the knee is not lost. Some of these nonoperative treatments are:
- Bracing: Protection of the knee from instability and any further damage due to impact is done by bracing combined with crutches to prevent excess weight bearing.
- Physical therapy: Specific exercises are advised once the swelling subsides for restoring the function of the knee and strengthening the muscle.
Surgical management:
- Reconstruction of the ligament: The ACL needs to be reconstructed to restore knee stability. The orthopaedic surgeon replaces the torn ligament with a graft of tissue on which a new ligament can grow.
- Types of ACL surgery grafts: The graft for ACL reconstruction may be taken from different places within the knee or from a deceased donor as deemed fit. These may be:
- Patellar tendon: Tendon between the kneecap and the shinbone
- Hamstring tendon: Tendon behind the thigh
- Quadriceps tendon: Tendon from kneecap into the thigh
What is Arthroscopic ACL reconstruction surgery?
In arthroscopic ACL reconstruction surgery is a procedure wherein the surgeons make small incisions and use an arthroscope to replace or repair a torn anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). Arthroscopic surgery is beneficial because it is less invasive and thus offers the following benefits:
- Less post-operative pain
- Reduced post-surgery hospital stay
- Quicker recovery
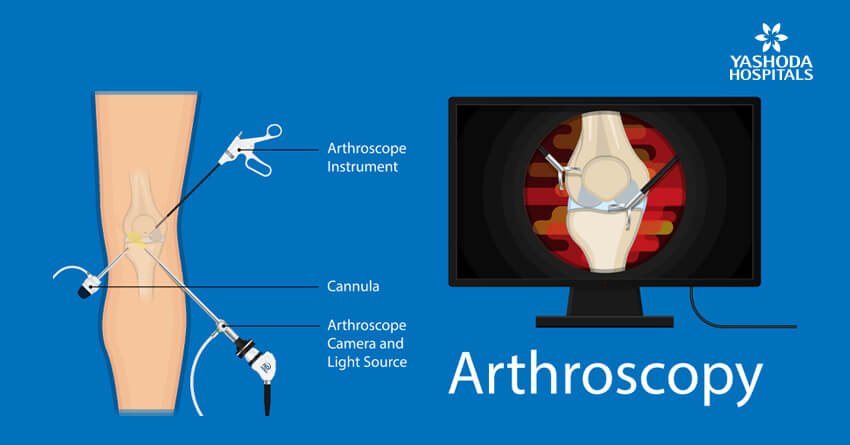
How is the arthroscopic ACL reconstruction surgery performed?
The surgery is done under anaesthesia. The surgical procedure takes around one to one-and-a-half hours (60 – 90 minutes).
- During the surgery, the orthopaedic surgeon first removes the damaged ligament and then replaces it with a piece of tendon graft.
- The graft is accurately positioned with screws and fixation devices by drilling sockets into the thighbone and shinbone.
- Post recovery from anaesthesia, the person is usually helped to practice walking with crutches with or without and a knee brace or splint.
- Prior to discharge, the person is given specific instructions regarding:
- Control of swelling and pain with medication and precautions like leg elevation, ice application and rest.
- Duration of crutches use and extent of weight bearing.
- Day to day activities like showering or bathing
- Wound care like the change of dressings etc
What is the recovery time for ACL reconstruction surgery?
A progressive physical therapy post ACL surgery is important for muscle strengthening and restoring flexibility. Post-surgery, a physical therapist advises exercises to be done under supervision or at home. It is advisable to adhere to the rehabilitation plan for the best outcomes and quicker recovery. While crutches to walk may be required for a couple of days to two weeks, full recovery generally takes about nine to 12 months or sometimes more before a person can return to complete normalcy and routine physical activities.
What are the factors affecting the cost of ACL reconstruction surgery?
The cost of ACL reconstruction surgery depends on many factors like:
- Location of the hospital and expertise available.
- Any associated complications and the duration of the surgical procedure
- Underlying medical condition
- Length of stay in the hospital and consumables, investigations and medications required.
Where can one get best quality ACL Reconstruction Surgery in Hyderabad? Who are the best orthopaedic surgeons in Hyderabad?
The Center for Orthopaedics at Yashoda hospital provides comprehensive orthopaedic care with scientific evidence based latest treatment regimens and technology. The team is led by internationally acclaimed best orthopaedic surgeons, trained nursing staff, medical & rehabilitative specialists, occupational and physical therapists. The orthopaedic centre also houses a state of art physiotherapy department to provide rehabilitative support.
References:
- Mayo Clinic. ACL Reconstruction. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/acl-reconstruction/about/pac-20384598. Accessed on March 10, 2019
- American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons. Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries. Available at.https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/anterior-cruciate-ligament-acl-injuries/. Accessed on March 10, 2019
- Hospital For Special Surgery. Avascular Necrosis (AVN Osteonecrosis). Available at.https://www.hss.edu/condition-list_avascular-necrosis.asp.Accessed on March 11, 2019
- US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health. ACL reconstruction. Available at https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007208.htm.Accessed on March 10, 2019
- Yashoda Hospital. Orthopaedic Treatments and Procedures. Available at. https://dev.yashodahospitals.com/specialities/orthopedics/treatments-and-procedures/.Accessed on March 10, 2019
About Author –
Dr. Shashi Kanth G, Sr. Consultant Orthopedic Surgeon, Yashoda Hospitals, Hyderabad
He is specialized in arthroscopy, sports medicine, and orthopedics. His expertise includes Lower Limb Joint Replacement Surgery, Lower Limb Arthroscopy, Sports Injuries, Foot and Ankle Surgery, & Management of Complex Trauma.















 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More