All you need to know about Heart Valve Diseases
What are heart valve diseases?
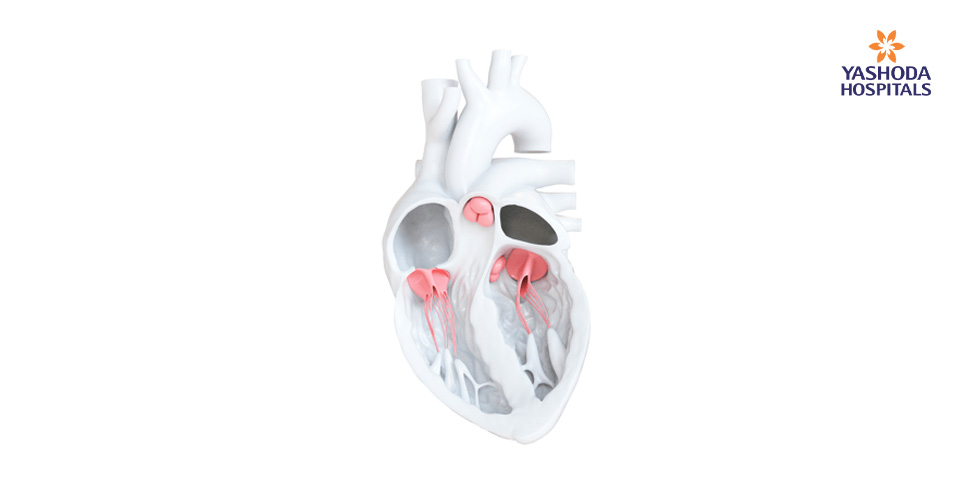
Heart valve disease is a condition wherein one or more of the heart valves are working as expected. The human heart has four valves which open and shut in sync with the heart’s rhythm. Heart Valves play a very important role in ensuring blood flows in the correct direction within and out of the heart in order to ensure that the human body receives proper blood supply.
The four valves of the heart are Aortic Valve, Mitral Valve, Pulmonology Valve, and Tricuspid Valve. Heart valve diseases are not uncommon and seen equally in children, adults and the elderly. The heart valves lie at the exit of each of the four heart chambers. The values help in one-way blood flow through your heart. The heart ensures that the blood flows in the forward direction only.
During the heartbeat, the ventricles and auricles expand as well as contract. When the ventricles are full, the mitral and tricuspid valves are kept shut. When the ventricles start contracting, the blood flows to the pulmonary artery and lungs through pulmonic and aortic valves. Different valve diseases are Valvular Stenosis, Valvular Insufficiency, Congenital Valve Disease, Bicuspid Aortic Valve Disease, Acquired Valve Disease, and Mitral Valve Prolapse (MVP).
What are the causes of other heart valve diseases?
Each valve disease has a different set of causes. Congenital Valve Disease is due to the wrong size of the aortic or pulmonic valves. Bicuspid aortic valve disease is due to the inability of the aortic valve to open and close properly. Acquired valve disease is caused due to a variety of diseases or infections due to rheumatic fever or endocarditis. Mitral valve prolapse is characterized by leaking valves and affects the functioning of the leaflets of the mitral valve.
What are the symptoms of heart valve diseases?
When a heart valve gets dysfunctional, the patient may experience typical symptoms like chest pain, palpitations, shortness of breath, fatigue, weakness, inability to maintain regular activity level, or even light-headedness. Valve diseases are usually characterized by shortness of breath, difficulty in breathing, weakness or dizziness, heart murmur, discomfort in the chest, palpitations, swelling of ankles and feet, and weight gain (two to three pounds in one day).
What are the risk factors & complications of heart valve diseases?
Some of the major risk factors for heart valve disease are the age of the person, unhealthy blood cholesterol levels, high blood pressure, smoking, insulin resistance, intravenous drug use, diabetes, overweight or obesity, lack of physical activity, and a family history of early heart disease.
How is heart valve disease diagnosed?
The disease can be diagnosed by an experienced cardiologist by primarily studying the Echocardiogram (‘Echo’), CT angiogram and a few other tests.
Echocardiography is the main test for diagnosing heart valve disease. Usually, the EKG (electrocardiogram) or chest x-ray is used to study possible signs of the heart valve condition. If the doctor suspects the occurrence of heart valve disease, echocardiography is done to confirm the same.
Other tests advised by the doctor include cardiac catheterization, transesophageal echocardiogram or TEE, stress testing, or cardiac MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). These additional tests and procedures help the cardiologist to better assess the severity of the condition and plan for the right course of treatment.
What are the treatments for heart valve diseases?
Heart valve disease is a lifelong condition. There is no complete cure for it. However, lifestyle changes and medicines can be of help in the treatment of symptoms and delay the complications of heart valve disease. The doctor may advise for having heart valve repair or replacement which depends on a number of factors like, the severity of the heart valve disease, and the age and general health of the patient.














 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More