A rare disorder of the blood-coagulation system, causing extensive microscopic clots
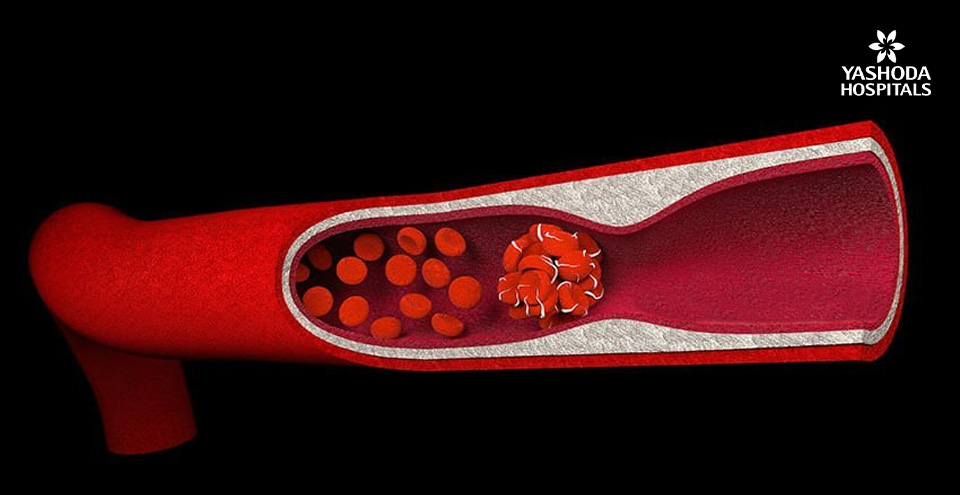
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura refers to a condition of the blood with low platelet count. This is a blood disorder marked by blood clots in small blood vessels.
CAUSES
A protein that aids in blood clotting is considered to be responsible for Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. This condition is marked by abnormal clotting of the blood, with platelets clumping together as clots, leading to bleeding under the skin, and preventing oxygen from reaching other parts of the body. Blood clots may appear due to cancer, chemotherapy, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, HIV infection, hormone replacement therapy and certain medications.

SYMPTOMS
The symptoms of Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura include bleeding of the skin or mucus membranes, feeling confused and weak, having a lot of fatigue and headache, reeling under shortness of breath, having a pale colour or yellowish skin, and developing faster heart rate (more than 100 beats per minute).
RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura may result in kidney failure, low platelet count (thrombocytopenia), low red blood cell count, nervous system problems, severe bleeding and stroke.
TESTS AND DIAGNOSIS
The doctor advises for blood and urine examination. Focus of the lab technician is on blood smear, CBC, Creatinine, and platelet count of the blood. The bilirubin levels are examined, in particular. Also, the focus of the diagnostic tests is to assess the lactate dehydrogenase level (LDH), urinalysis and von willebrand factor assay.
TREATMENTS
The usual treatment for Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura is plasma exchange, the process in which abnormal plasma is replaced by normal plasma from a healthy donor. Plasma contains blood cells and platelets. By plasma exchange, the protein triggers responsible for Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura are also removed. The blood tests are continued to study the condition of the blood plasma.














 Appointment
Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More