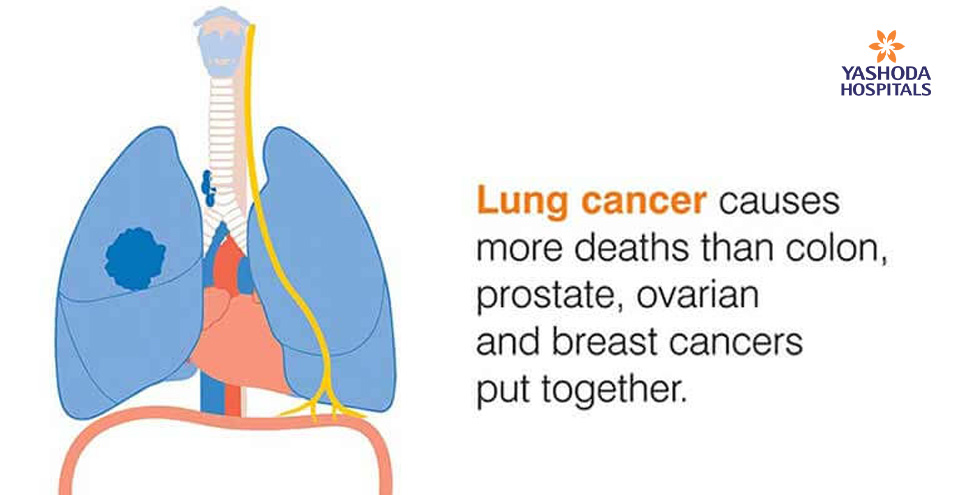
treatment of lung cancer
The cancer treatment plan is dependent on several factors, such as a person’s overall health, the type and stage of cancer, and individual preferences. The available treatment options are conservative or surgical as follows:
Surgery: Lung cancer and a margin of healthy tissue are removed during the surgical procedure in one of the following ways:
- Lobectomy: Surgical removal of the affected lobe of the lung
- Pneumonectomy: Surgical removal of entire lung
- Segmental resection: Surgical removal of a substantial portion, but usually less than the lobe from the lung
- Wedge resection: Surgical removal of a small part of the lung including the cancerous part and some adjacent healthy tissue
Sometimes the surgeon may also remove lymph nodes from a person’s chest to observe them for signs of cancer.
Surgery is usually considered in cases where the cancer is confined to the lungs. In cases where the lung cancer spreads to faraway tissues or the extent of the cancer is larger chemotherapy or radiation therapy may be recommended before the surgery. This procedure helps in reducing the size of cancer by shrinkage. Chemotherapy or radiation therapy may also be recommended after the surgery if it is suspected that the cancer cells have been left behind after the surgery or if the recurrence of cancer is suspected.
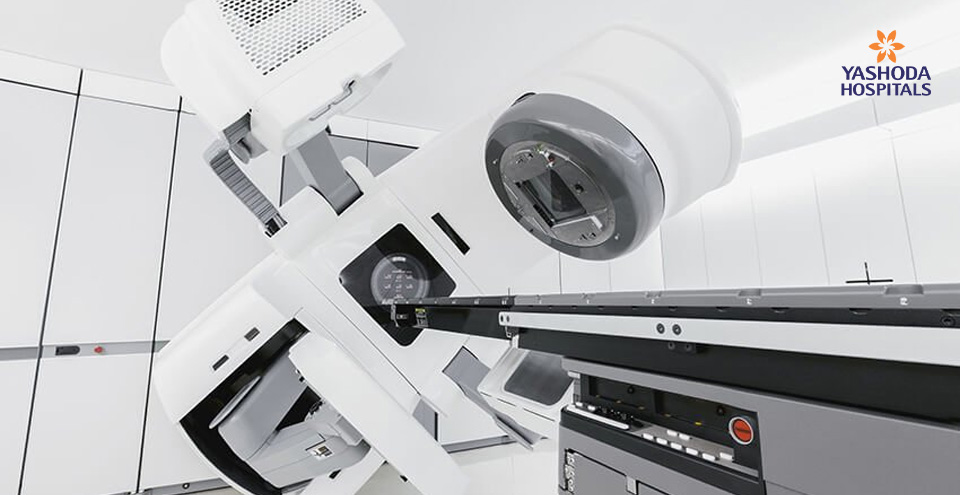
Radiation therapy: This procedure makes use of high-powered energy beams from sources such as X-rays and protons for destroying the cancer cells. In cases of locally advanced lung cancer, radiation may be recommended before or after surgery. It is also combined with chemotherapy in cases where surgery is not feasible or where the cancer is advanced to farther tissues.
Chemotherapy: Drugs are used to destroy cancer cells in chemotherapy. It may consist of a single drug or more drugs in a combination that may be administered intravenously, or they are taken orally. Chemotherapy is given in cycles over a period of weeks or months, with or without radiotherapy. Breaks in between consecutive cycles are given to allow recovery.
Radiosurgery or Stereotactic body radiotherapy: It is an intense radiation treatment in which the cancer cells are targeted to be destroyed with many beams of radiation from different angles. It is completed in one or more cycles. It is often recommended for persons who cannot undergo surgery or for the treatment of lung cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, including the brain.
Targeted drug therapy: Specific abnormalities present within cancer cells are targeted by the therapeutic agent or drug being used. The cancer cells are destroyed by blocking such abnormalities. Sometimes only persons with specific gene mutations may be responsive to targeted therapies. Such persons are identified after laboratory testing of their genetic material before treatment is initiated.
Immunotherapy: The body’s inherent defense capability or immune system is made use to fight cancer. Cancer cells produce proteins that blind the immune system cells. As a result, the person’s immune system does not recognize and fight the cancer cells. Immunotherapy evokes the body’s response by interfering with that process.
Palliative care: Supportive or palliative care involves a multidisciplinary team working with a doctor to minimize the signs and symptoms of the disease and improve a person’s quality of life.

⇒ Oncology rehabilitation: A wide range of therapies that are designed as per the needs of a person help in building strength and endurance, reducing stress and maintaining normal energy levels and regaining independence to carry out important daily living activities that constitute oncology rehabilitation.
Some of the rehabilitation therapies are:
- Physical therapy: Physical therapists help a person design personalized exercise programs that are a mix of range-of-motion training with light resistance exercises. Physical activity helps in overcoming fatigue and improving physical function and overall well-being.
- Occupational therapy: Occupational therapists help a person design a personalized plan to continue with their important daily living activities such as dressing, showering, and eating to maintain a good quality of life.
- Speech and language therapy: Many times, persons with cancer may have adverse effects on their speech and language. Speech and language therapists help a person address complications that may affect their speech, cognitive and language abilities like dryness of mouth, difficulty in swallowing, loss of voice, etc.
- Manual therapy: Massage therapy techniques may be considered to overcome cancer-related pain and improve a person’s quality of life during cancer treatment.
⇒ Nutrition support: Many cancer patients undergo poor gastrointestinal experience symptoms. A nutritional support team should work with persons with lung cancer to help
- Restore digestive health
- Prevent malnutrition and nutrient deficiencies, during treatment.
It is extremely important to stay physically strong and nourished to continue with intense cancer treatment. A dietitian may be required to conduct a comprehensive nutritional assessment and determine daily goals for calories and protein, and micronutrients like vitamins and minerals.
⇒ Pain management: Many factors like age, physical and mental status, type, and stage of cancer affect a person’s pain threshold. Cancer may cause pain itself, or it may arise due to collateral reasons like:
- Blockage of blood vessels due to cancer which leads to compromised blood circulation.
- Dissemination of cancer cells may lead to blockage of an organ or tube within the body, for example, kidneys or bladder
- Side effects of different treatment like surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, etc
- Spread of cancer to other locations in the body like bones or compression/destruction of nerve
Pain management strategies are adopted as a part of the overall treatment to improve a person’s quality of life. Some pain management modalities are:
- Prescription medications
- Nerve block therapies
- Physical therapy
- Massage therapy
- Relaxation techniques and guided imagery
⇒ Lymphedema prevention and treatment: Acondition in which excess lymphatic fluid collects in the interstitial tissue leading to swelling in various areas of the body. Though it is usually seen in the arms or legs, swelling may also be seen in other parts of the body, like breast or chest wall.
Lymphedema may either develop due to cancer or maybe a consequence of cancer treatment like surgery where many lymph nodes are removed. In certain cases, it may be a result of factors that change, block, or interrupt the flow of lymph fluid through the lymphatic system. Some of these factors may be infection, trauma, scar tissue.
Lymphedema that stays untreated may adversely affect function and mobility in the affected limb or may lead to infection, skin breakdown and other complications. Lymphedema may be prevented or controlled with proper care and treatment. Depending on the severity and cause, lymphedema care may vary from person to person.
Some of the treatment options for the management of lymphedema may include:
- Skincare
- Manual lymph drainage
- Gentle massaging
- Light physical exercises for stimulating the lymphatic system
- Use of additional aids like compression bandages, garments like sleeves and stockings for preventing the accumulation of additional fluid in the tissue.
- Sometimes medications may be prescribed to reduce inflammation, prevent blood clots, and treat infections.
- Surgical options for the treatment of lymphedema may be recommended in extreme cases where conservative options fail.
What can a person do to reduce the risk of lung cancer?
There is no sure way to prevent lung cancer, but a person can reduce the risk of developing lung cancer by lifestyle modifications like;
- Don’t consider smoking: A non-smoker should stay away from smoking and never consider starting it. Similarly, younger family members like children should be educated on the bad effects of smoking so that they do not yield under peer pressure.
- Stop smoking: If you are a smoker, you should consider stopping to smoke immediately. Even if a person has been a smoker for a long duration of time, quitting at any point reduces the risk of developing lung cancer considerably. A doctor can be consulted for effective strategies and information on smoking deaddiction aids that can help in quitting.
- Avoid exposure to second-hand smoke: Living or working near a smoker can increase a person’s risk of lung cancer from second-hand smoke. In such cases, the smoker should be encouraged to quit smoking or at least smoke away from other persons.
- Avoiding workplace carcinogens: If a person is employed in a place where harmful elements, gases or chemicals are handled, adequate precautions must be taken for self- protection from exposure to such toxins. Personal protective equipment like a face mask should never be avoided. The risk of lung damage due to exposure to carcinogens becomes manifold if the person smokes.
- Adopt healthy dietary habits: A healthy diet with a variety of fruits and vegetables should be consumed. Natural sources of vitamins and nutrients are the best option. Supplements like vitamins should be reserved for prescription by a doctor and in a situation where the dietary requirements are not fulfilled.
- Exercise regularly: If work or family commitments don’t allow a person to exercise daily and regularly, he/she should start slowly. Exercising most days of the week can prove to be beneficial for the overall health of the person.
References:
- American Cancer Society. Radon and Cancer. Available at: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/cancer-causes/radiation-exposure/radon.html. Accessed on December 08, 2019
- Centre for disease control and prevention.Lung Cancer. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/lung/. Accessed on December 08, 2019
- Mayo Clinic. Lung cancer. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/lung-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20374620. Accessed on December 08, 2019
- NIH National cancer institute. Lung Cancer. Available at: https://www.cancer.gov/types/lung. Accessed on December 08, 2019
- Lung cancer. Available at:https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/lung-cancer/.Accessed on December 08, 2019
- Cancer treatment centers of America.Lung cancers. Available at. https://www.cancercenter.com/cancer-types/lung-cancer. December 08, 2019
Patient Testimonials For Cancer






























 Appointment
Appointment Second Opinion
Second Opinion WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More





