Cystic fibrosis
Causes, symptoms, complications, diagnosis, treatments
All you need to know about Cystic Fibrosis
What is Cystic fibrosis?
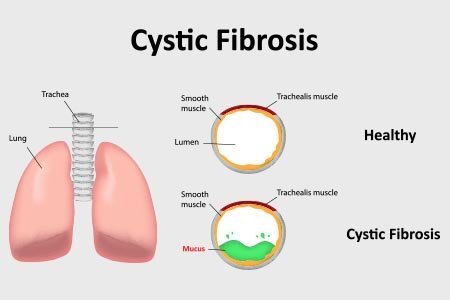
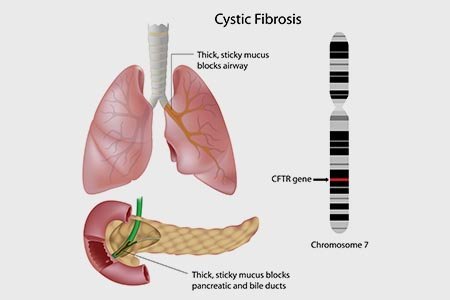
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a progressive genetic disorder which causes body to produce thick mucus, primarily affecting respiratory system and digestive system. Particularly, cystic fibrosis may affect lungs, pancreas, liver, gall bladder and intestines. Other organ systems affected are genitourinary system and reproductive system.
In healthy individuals, the secreted fluids such as sweat, mucus and digestive juices are thin and free-flowing. In patients with cystic fibrosis, the fluid is sticky and thick. As a result, the tubes and ducts in these organs become clogged.
What is Cystic Fibrosis?
What are the causes of cystic fibrosis?
Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disorder. The CTFR gene that lies on chromosome 7 controls the movement of salts (sodium/chloride), thus governs the movement of water and consistency of the secretions from these cells.
Mutation of this gene predispose to the poor movement of salt and water across the cells and thus cause thickening of the mucus. The thickened mucus along the lining of the exocrine ducts and lumen are the hallmark presentation of cystic fibrosis.
Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disease which often passes from one generation to another. The child may suffer from cystic fibrosis only if he/she receives gene error from both father and mother. In case, the child receives a defective gene from just one parent, the child will then be a carrier without any clinical presentation. The gene carriers may possibly pass it on to their children.
What are the Cystic Fibrosis Symptoms?
Cystic fibrosis affects multiple organs, therefore, signs and symptoms may differ from person to person, depending on the organ system involved. These include:
- Frequent lung infections
- Persistent coughing and wheezing with thick mucus
- Infertility in male patients. Female patients have thick cervical mucus, thus making conception harder.
- Big appetite but poor weight gain; malnutrition
- Severe constipation; bulky, smelly and greasy bowel movements
- Sticky stool with a foul smell
- Very salty sweat
- Wheezing or shortness of breath
What are the complications of cystic fibrosis?
Respiratory system:
- Nasal polyps and sinusitis
- Production of blood while coughing
- Recurrent pneumonia or respiratory infections
- Obstructive lung disease (emphysema)
- Chronic nasal congestion and infections
Digestive system:
- Diabetes
- Pancreatitis
- Distal intestinal obstruction syndrome (DIOS)
- Gallstones
- Liver diseases
- Rectal prolapse
Thinning of bones and cross infection (possibility of acquiring infections from others or transferring infections to others) are other commonly noticed complications of cystic fibrosis.
What are the precautions for patients with cystic fibrosis?
People with cystic fibrosis need a high level of attention and care. The lifestyle changes for patients with cystic fibrosis aim to prevent the infections and improve lung and overall health. Some recommendations include:
- Avoiding exposure to dust, smoke, harmful chemicals etc.
- Ensuring adequate fluid intake
- Engaging in physical activity as advised by the treating doctor
- Regular clearing of mucus from the airways to prevent the blockade
- Taking a healthy, nutritious diet
- Salt supplements in hot weather; patients with cystic fibrosis deplete salts faster than normal individuals.

Precautions for Patients with Cystic Fibrosis
How is Cystic fibrosis diagnosed?
Depending on the organ system affected, the concerned specialists i.e. pediatricians, pulmonologists, gastroenterologists or physicians can diagnose the condition.
The doctor performs the following tests for diagnosing cystic fibrosis:
– Medical history
– Physical examination
– Tests
- Sweat test to determine the salt content in sweat
- Screening test to check the levels of immune-reactive trypsinogen (IRT) chemical
- Genetic test to confirm the diagnosis
- Other tests as required
- – Chest X-ray
- – Fecal fat test
- – Lung function test
Diagnosis for Cystic Fibrosis
How is Cystic fibrosis treated?
Due to the involvement of multiple organ systems, cystic fibrosis can be a complex disease to manage.
Patients need immediate attention to respiratory implications such as lung infection, thick sticky mucus; and intestinal implications such as intestinal blockage, nutrition and dehydration.
Though treatment requirements depend on a multitude of factors like the severity of the disease and the overall health of the patient, some of the commonly used modalities are:
- Medications
- Airway clearance: To remove the plugged mucous
- Pulmonology rehabilitation: To improve lung function and health, including activities like physical exercise, breathing techniques and nutritional counseling. Rehabilitation may involve chest physical therapy, energy conserving techniques and psychological counseling.
- Lung transplant is suggested in severe cases if required.
- Digestive care: Mucus-thinning medicines, oral pancreatic enzymes and nutritional counseling. Sometimes surgery may be necessary to remove intestinal blockages.
To know more about cystic fibrosis, you can request a callback and our experts will call you and answer all your queries.
References
- Mayo Clinic. Cystic Fibrosis. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cystic-fibrosis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353706. Assessed on 08 March 2018.
- Cystic Fibrosis Trust. What is Cystic Fibrosis? Available at: https://www.cysticfibrosis.org.uk/what-is-cystic-fibrosis. Assessed on 08 March 2018.
- OMICS International. Pulmonology Fibrosis and Cystic Fibrosis. Available at: https://www.omicsonline.org/conferences-list/pulmonary-fibrosis-and-cystic-fibrosis.Assessed on 08 March 2018.
- Cystic Fibrosis. Available at: https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000107.htm. Assessed on 08 March 2018.
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. Cystic Fibrosis. Available at: https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/cystic-fibrosis#. Assessed on 008 March 2018
Disclaimer:
“The content of this publication has been developed by a third party content providerwho are clinicians and/or medical writers and/or experts. The information contained herein is for educational purpose only and we request you to please consult a Registered Medical Practitioner or Doctor before deciding the appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan.”



 Appointment
Appointment Second Opinion
Second Opinion WhatsApp
WhatsApp Call
Call More
More





